2025-07-10 京都大学
<関連情報>
- https://www.kyoto-u.ac.jp/ja/research-news/2025-07-10-0
- https://www.kyoto-u.ac.jp/sites/default/files/2025-07/web_2507_Matsunaga-a12b7b05459c38c98cbe3dcffe444b1a.pdf
- https://www.pnas.org/doi/abs/10.1073/pnas.2502713122
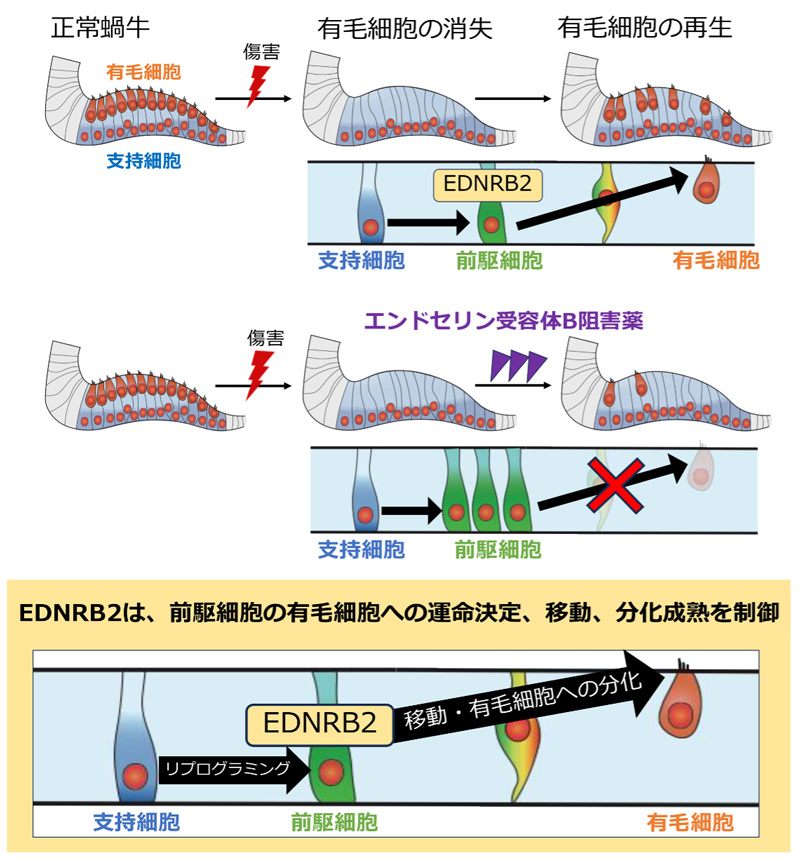
EDNRB2 は⿃類蝸⽜感覚上⽪の有⽑細胞再⽣過程において前駆細胞の運命決定、移動、分化を制御する EDNRB2 regulates fate, migration, and maturation of hair cell precursors in regenerating avian auditory epithelium explants
Marie Takeuchi, Mami Matsunaga, Tomoko Kita, +4 , and Takayuki Nakagawa,
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences Published:July 8, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2502713122
Significance
The auditory epithelium consists of two cell types: sensory hair cells (HCs) and surrounding supporting cells (SCs). Mammalian SCs lose their ability to regenerate HCs after birth, whereas avian SCs retain this potential throughout their life span. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying HC regeneration in the avian auditory epithelia remain largely unknown. This study uncovered a mechanism for HC regeneration in the auditory epithelium. Endothelin receptor type B2 (EDNRB2) regulates fate, migration, and maturation of HC precursors during spontaneous HC regeneration in the avian auditory epithelium explants, providing insights into inducing HC regeneration in the inner ear of mature mammals.
Abstract
The mammalian cochlea loses its ability to regenerate hair cells (HCs) after birth. In contrast, in the avian auditory epithelium, the basilar papilla (BP), supporting cells (SCs) retain the capability for HC regeneration throughout life. Our previous study using single-cell RNA sequencing indicated a stepwise fate conversion of SCs to HCs via a precursor state, in which endothelin receptor type B2 (EDNRB2) exhibited specifically high expression during HC regeneration in chick BP. This study aimed to reveal the distinct role of EDNRB2 in HC regeneration in the chick BP. During HC regeneration in chick BP explant cultures, EDNRB2 expression was observed in some ATOH1-expressing SCs immediately after HC loss and decreased as the HC regeneration process progressed. In the embryonic chick BP, EDNRB2 expression was specifically detected in the precursor cell state, confirming that mature SCs were reprogrammed to the precursor state in response to HC loss. Pharmacological inhibition of EDNRB signaling decreases the number of regenerated HCs in chick BP explant cultures. RNA sequencing revealed that EDNRB signaling inhibition downregulated genes involved in HC differentiation and maturation as well as genes involved in cell migration. Histological assessments clarified the deterioration of HC precursor migration and the delay in HC regeneration due to EDNRB signaling inhibition. These results indicate that EDNRB2 expression contributes to the fate determination of HCs, and its signaling regulates the migration and maturation of HC precursors during chick HC regeneration.


