2025-07-23 国立循環器病研究センター
<関連情報>
- https://www.ncvc.go.jp/pr/release/pr_48258/
- https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/STROKEAHA.125.050859
隠れた血管性脳損傷と臨床的特徴を用いた長期抗血栓療法の最適化予測モデル Prediction Model to Optimize Long-Term Antithrombotic Therapy Using Covert Vascular Brain Injury and Clinical Features
Kaori Miwa, MD, PhD, Kenta Tanaka, MS, Masatoshi Koga, MD, PhD, Kanta Tanaka, MD, PhD, Yusuke Yakushiji, MD, PhD, Makoto Sasaki, MD, PhD, Kohsuke Kudo, MD, PhD, …,
Stroke Published 19 June 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.125.050859
Abstract
BACKGROUND:
Defining the risk of developing major bleeding, especially intracranial hemorrhage (ICH), or ischemic stroke (IS) in patients receiving antithrombotic therapy is crucial. Existing risk prediction tools would inadequately assess the net clinical benefit of antithrombotic therapy. We aimed to develop novel risk scores incorporating covert vascular brain injury to personalize the risk assessment of major bleeding, ICH, and IS in patients receiving antithrombotic therapy.
METHODS:
The prospective, multicenter, observational study (BAT2 [Bleeding With Antithrombotic Therapy Study-2]) enrolled patients receiving oral antiplatelets or anticoagulants from 52 hospitals across Japan between 2016 and 2019. Multimodal brain magnetic resonance imaging was performed at baseline under prespecified conditions to determine cerebral small vessel disease (white matter hyperintensity, cerebral microbleed, lacune, enlarged perivascular space, and cortical superficial siderosis), nonlacunar infarct, and intracranial artery disease with central reading. Risk scores, collectively termed the BAT2 scores, were developed separately to evaluate the comparative risks of (1) major bleeding, (2) ICH, and (3) IS based on covariates from Cox proportional hazards models and clinical relevance. Model performance was assessed with the Harrell C-index and calibration slope adjusted for optimism via bootstrapping.
RESULTS:
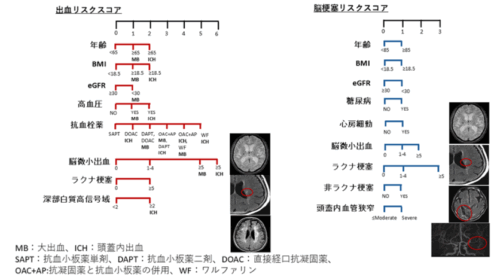
Of 5378 patients enrolled, 5250 were analyzed (mean age, 71±11 years, 33% women); 93 experienced major bleeding, including 55 had ICH, and 197 had IS during a median follow-up of 2.0 years. Predictors for bleeding included age, underweight, renal impairment, hypertension, cerebral microbleed, lacune, and antithrombotic treatment type. Predictors for ICH further included deep white matter hyperintensity but not renal impairment. For IS, predictors included age, renal impairment, diabetes, atrial fibrillation, lacune, cerebral microbleed, nonlacunar infarct, and intracranial artery disease. Prediction performance showed optimism-adjusted C-index and calibration slope of 0.69 (95% CI, 0.64–0.74) and 0.82 (95% CI, 0.62–1.06) for bleeding, 0.75 (95% CI, 0.67–0.80) and 0.80 (95% CI, 0.56–1.02) for ICH, and 0.64 (95% CI, 0.60–0.68) and 0.92 (95% CI, 0.73–1.18) for IS.
CONCLUSIONS:
The BAT2 scores may help optimize the balance between risks and benefits of antithrombotic therapy.
REGISTRATION:
URL: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov; Unique identifier: NCT02889653. URL: https://www.umin.ac.jp/ctr; Unique identifier: UMIN000023669.