2025-08-21 カリフォルニア大学ロサンゼルス校(UCLA)
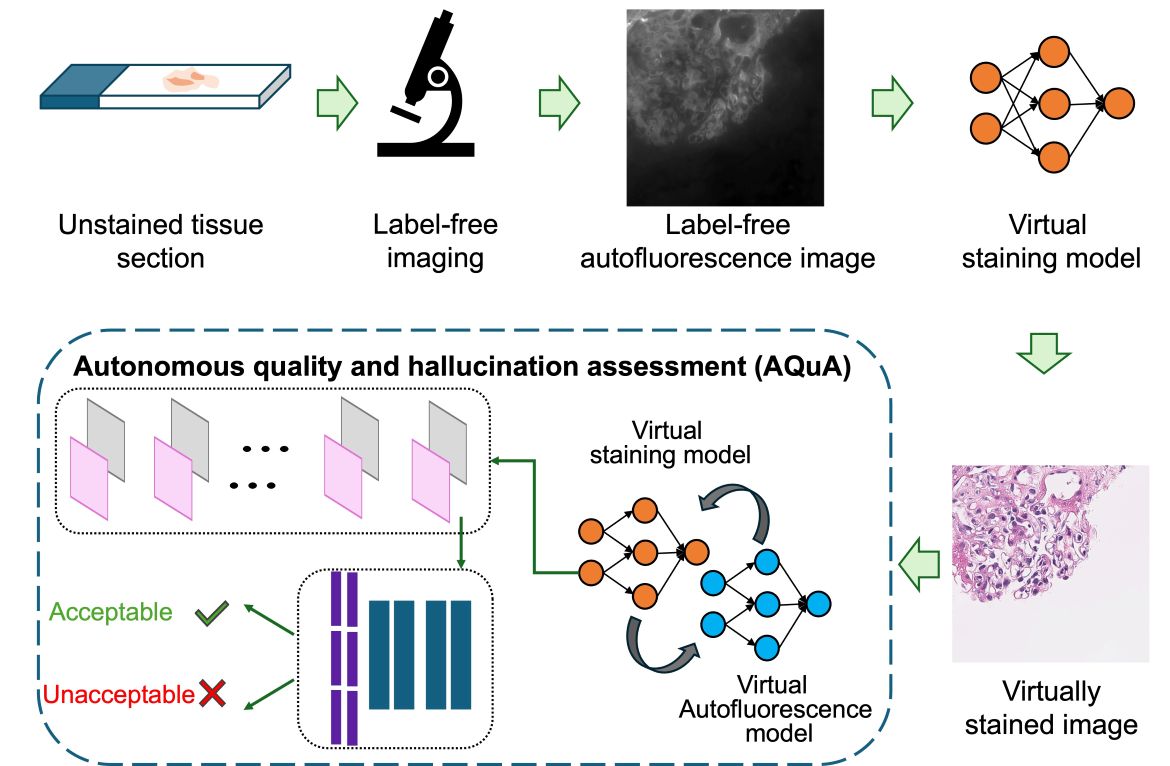 A diagram summarizes the machine learning process behind a UCLA-developed AI system for finding potentially dangerous errors in virtual staining.
A diagram summarizes the machine learning process behind a UCLA-developed AI system for finding potentially dangerous errors in virtual staining.
<関連情報>
- https://newsroom.ucla.edu/releases/dangerous-AI-errors-digital-pathology-caught-ucla-artificial-intelligence
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41551-025-01421-9
バーチャル組織染色とデジタル病理学における幻覚検出のための堅牢でスケーラブルなフレームワーク A robust and scalable framework for hallucination detection in virtual tissue staining and digital pathology
Luzhe Huang,Yuzhu Li,Nir Pillar,Tal Keidar Haran,William Dean Wallace & Aydogan Ozcan
Nature Biomedical Engineering Published16 June 2025
DOIhttps://doi.org/10.1038/s41551-025-01421-9
Abstract
Histopathological staining of human tissue is essential for disease diagnosis. Recent advances in virtual tissue staining technologies using artificial intelligence alleviate some of the costly and tedious steps involved in traditional histochemical staining processes, permitting multiplexed staining and tissue preservation. However, potential hallucinations and artefacts in these virtually stained tissue images pose concerns, especially for the clinical uses of these approaches. Quality assessment of histology images by experts can be subjective. Here we present an autonomous quality and hallucination assessment method, AQuA, for virtual tissue staining and digital pathology. AQuA autonomously achieves 99.8% accuracy when detecting acceptable and unacceptable virtually stained tissue images without access to histochemically stained ground truth and presents an agreement of 98.5% with the manual assessments made by board-certified pathologists, including identifying realistic-looking images that could mislead diagnosticians. We demonstrate the wide adaptability of AQuA across various virtually and histochemically stained human tissue images. This framework enhances the reliability of virtual tissue staining and provides autonomous quality assurance for image generation and transformation tasks in digital pathology and computational imaging.