2025-09-10 愛媛大学
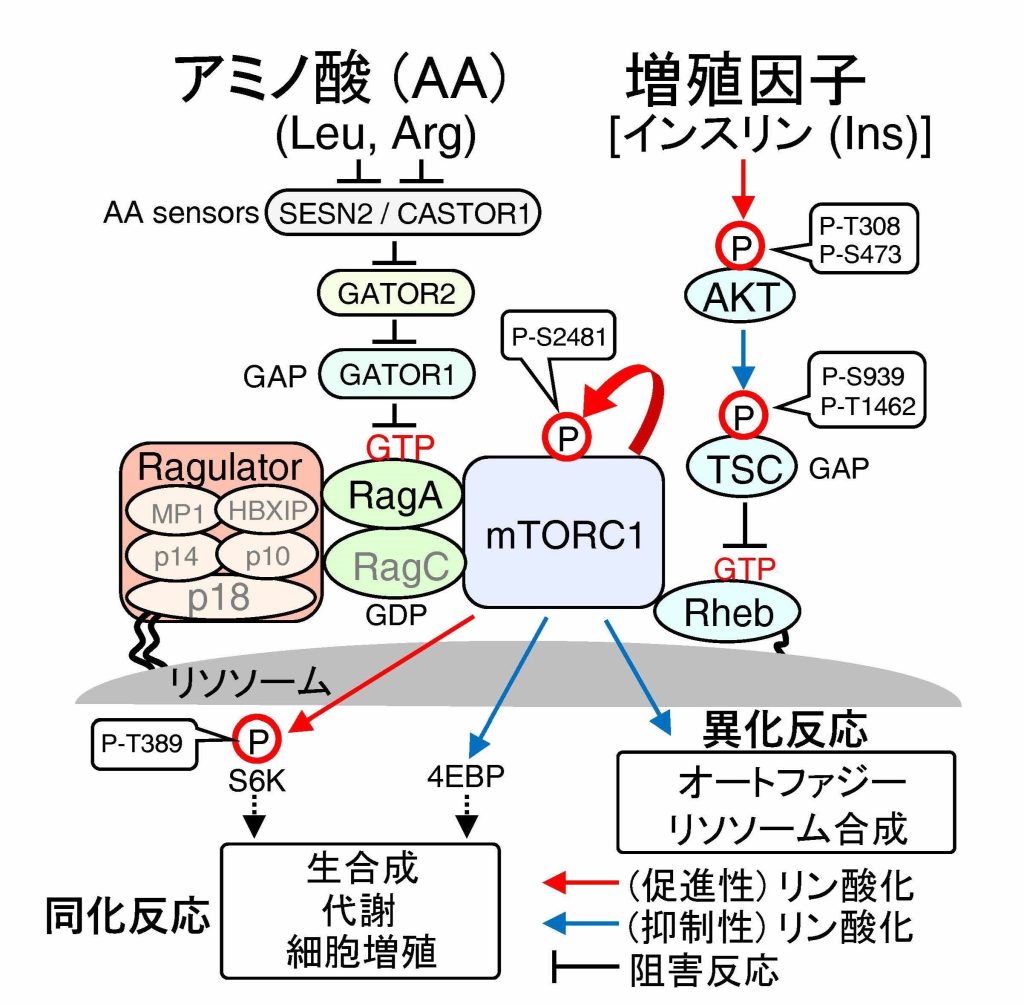
mTORC1栄養シグナル経路
<関連情報>
- https://www.ehime-u.ac.jp/data_relese/pr_20250910_med/
- https://www.ehime-u.ac.jp/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/pr_20250910_med.pdf
- https://www.life-science-alliance.org/content/8/11/e202503206
リソソームPP2AによるTSC2のアミノ酸濃度に依存した脱リン酸化がmTORC1栄養シグナル伝達を制御する Amino acid–dependent TSC2 dephosphorylation by lysosome–PP2A regulates mTORC1 signaling transduction
Takanori Nakamura, Shigeyuki Nada, Masaki Matsumoto, Nuha Loling Othman, Hidetaka Kosako, Kazuki Ikeda, Naohiko Koshikawa, Junya Masumoto, Tatsuya Sawasaki, Mutsuhiro Takekawa, Takashi Suzuki , Masato Okada
Life Science Alliance Published: 2 September 2025
DOI: 10.26508/lsa.202503206
Abstract
The mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) signaling pathway, composed of amino acid (AA)–sensing (Ragulator/LAMTOR-Rag) and growth factor (GF)–sensing (AKT-TSC1/2-Rheb) axes, pivotally regulates intracellular anabolism and catabolism. mTORC1 deregulation is associated with various metabolic diseases, including cancer and diabetes. As a key regulator of nutrient signaling, mTORC1 integrates a variety of nutrient signals. However, signal integration and crosstalk in the mTORC1 pathway remain incompletely understood. Therefore, in this study, we aimed to understand the complex mTORC1 signaling cascade by constructing an integrated mathematical model of temporal mTORC1 regulation using two AA-sensing and GF-sensing axes. Mathematical simulations and experimental data revealed robust AKT phosphorylation (P-T308/P-S473) after insulin stimulation, regardless of the intracellular AA levels. Conversely, AKT-mediated inhibitory TSC2 phosphorylation (P-T1462) substantially diminished during AA deprivation compared with AA treatment. Furthermore, we highlighted PP2A-mediated TSC2 dephosphorylation during AA removal, ensuring complete mTORC1 activation only upon concurrent AA and GF sensing. Thus, we elucidated mTORC1 signaling dynamics, revealing the complex interplay between AAs and GFs and offering insights into metabolic regulation.