2025-12-22 中国科学院(CAS)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research-news/202512/t20251229_1143280.shtml
- https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.analchem.5c01671
SpyCatcher-SpyTagを用いた膜タンパク質SPRアッセイのための堅牢な固定化法 A Robust Immobilization Method for Membrane Protein SPR Assays Using SpyCatcher-SpyTag
Li Yan, Chenchen Zhu, Yingkui Dong, Hongxin Zhao, Bo Wu, and Junfeng Wang
Analytical Chemistry Published August: 31, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.5c01671
Abstract
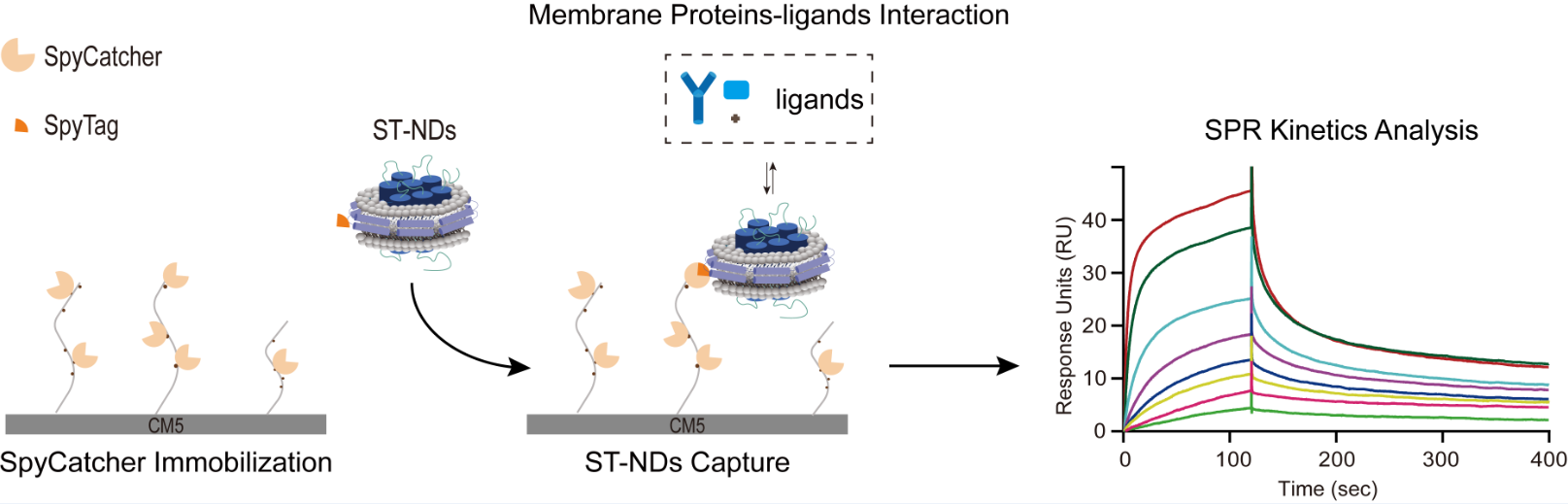
Membrane proteins are essential for numerous biological processes and constitute a significant portion of drug targets, making the study of their interactions with ligands crucial for drug discovery. Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) is a powerful, label-free technique for real-time biomolecular interaction analysis, but its application to membrane proteins is limited by inherent difficulties in immobilizing these proteins on sensor surfaces while preserving their native conformation and functionality. Lipid nanodiscs offer a promising solution by providing a native-like membrane environment. However, efficient and stable immobilization of nanodiscs on chip surfaces remains challenging. Here, we present a convenient and efficient approach utilizing the SpyCatcher-SpyTag system for the covalent immobilization of nanodiscs on SPR chips. This method ensures stable and specific attachment, enabling precise kinetic analysis of membrane protein interactions. We demonstrate the utility of this approach by applying it to study the interactions of Granuphilin C2A domain with PIP2 lipid, GPRC5D with an antibody, and VDAC1 with a small molecule inhibitor. This approach has the potential to advance the application of SPR in membrane protein interaction studies and drug discovery.