2026-01-16 スイス連邦工科大学ローザンヌ校(EPFL)
Credit: X. Li/ © 2026 EPFL
<関連情報>
- https://actu.epfl.ch/news/first-in-human-drug-trial-lowers-high-blood-fats/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-025-04169-6
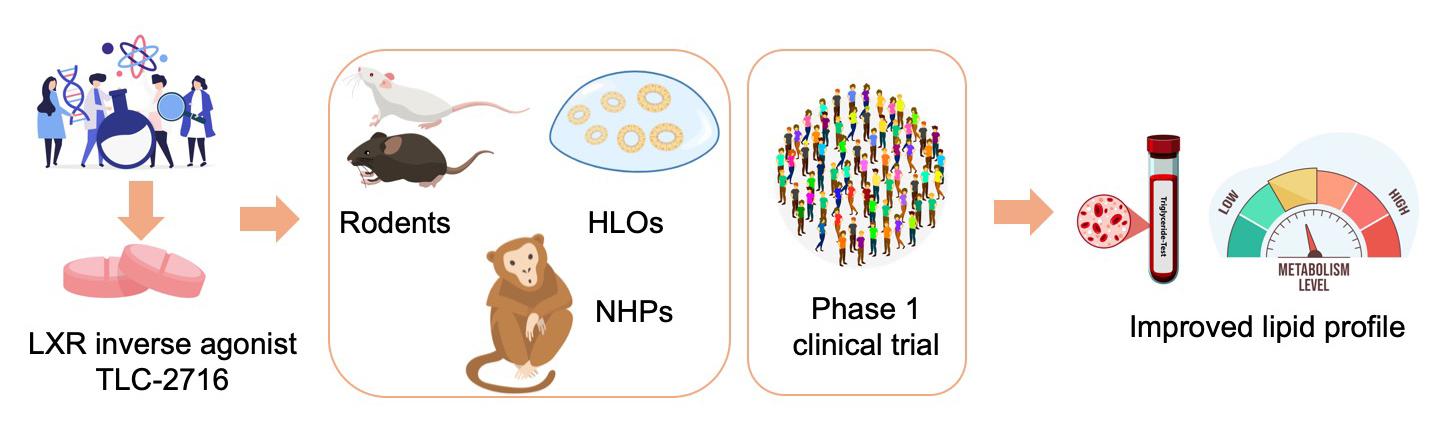
脂質異常症に対する経口投与可能な肝臓限定型LXR逆作動薬:前臨床開発および第1相試験 An oral, liver-restricted LXR inverse agonist for dyslipidemia: preclinical development and phase 1 trial
Xiaoxu Li,Giorgia Benegiamo,Archana Vijayakumar,Natalie Sroda,Masaki Kimura,Ryan S. Huss,Steve Weng,Eisuke Murakami,Brian J. Kirby,Giacomo V. G. von Alvensleben,Claus Kremoser,Edward J. Gane,Takanori Takebe,Robert P. Myers,G. Mani Subramanian & Johan Auwerx
Nature Medicine Published:16 January 2026
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-025-04169-6
Abstract
Despite advances in lipid-lowering treatment, atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease remains the leading cause of mortality, underscoring the need to address residual risk. Targeting both the synthesis and clearance of triglyceride (TG)-rich lipoproteins is a promising approach. Liver X receptor (LXR) repression can reduce plasma TG and cholesterol and improve insulin sensitivity by suppressing de novo lipogenesis and intestinal lipid absorption and enhancing clearance of TG-rich lipoproteins, but its clinical utility remains unexplored. Here we demonstrate the role of LXR inverse agonists in lipid metabolism and metabolic diseases in preclinical models and humans. Given concerns that systemic LXR repression may impair reverse cholesterol transport, we developed TLC-2716, an orally administered, gut- and liver-restricted LXR inverse agonist. In human liver organoids modeling steatohepatitis, TLC-2716 reduced lipid accumulation and suppressed inflammation and fibrotic gene expression. In a randomized, placebo-controlled phase 1 clinical trial, 14-day treatment with TLC-2716 was well tolerated (primary endpoints) and resulted in placebo-adjusted reductions up to 38.5% in plasma TG and 61% in postprandial remnant cholesterol (secondary endpoints). In conclusion, these results highlight the tolerability and therapeutic potential of TLC-2716 as a treatment for managing dyslipidemia and reducing residual atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk in humans. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT05483998.