持続可能で安価な方法は、商業的な応用の可能性がある Sustainable, cheaper method has potential for commercial applications
2022-07-28 テキサス A&M大学
PFASは環境中で容易に分解されず、微量であっても毒性があります。「人体への曝露や生態系への悪影響を防ぐために、除去・破壊する必要があります。
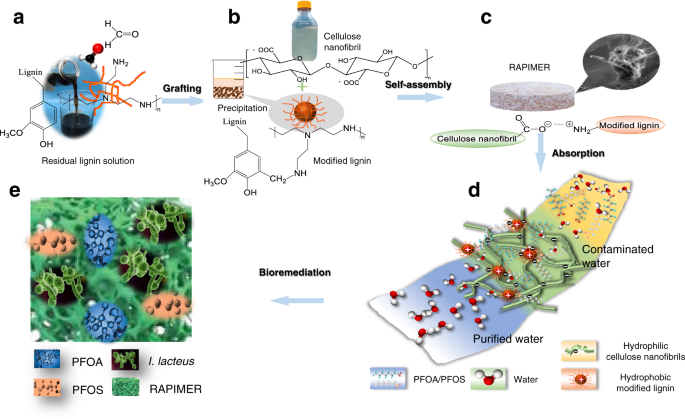
植物由来の材料を使用してPFASを吸着させ、食べる微生物菌でそれらを処分する技術を開発しました。
PFASは植物素材の細胞壁に吸着され、菌類が植物を食べるとき、吸着していた化学物質も食べてしまう。
これは、人の健康や生態系を守るために有害な化学物質を、無害で、より費用対効果の高い方法で除去する強力な可能性を持つ持続可能な処理システムである。
<関連情報>
- https://agrilifetoday.tamu.edu/2022/07/28/pfas-bioremediation-material-developed-by-texas-am-agrilife/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-022-31881-5
バイオミメティックな多機能リグノセルロースナノ骨格を用いた持続可能な環境修復技術 Sustainable environmental remediation via biomimetic multifunctional lignocellulosic nano-framework
Jinghao Li,Xiaohan Li,Yabin Da,Jiali Yu,Bin Long,Peng Zhang,Christopher Bakker,Bruce A. McCarl,Joshua S. Yuan &Susie Y. Dai
Nature Communications Published:28 July 2022
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-31881-5
Abstract
Chemical pollution threatens human health and ecosystem sustainability. Persistent organic pollutants (POPs) like per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are expensive to clean up once emitted. Innovative and synergistic strategies are urgently needed, yet process integration and cost-effectiveness remain challenging. An in-situ PFAS remediation system is developed to employ a plant-derived biomimetic nano-framework to achieve highly efficient adsorption and subsequent fungal biotransformation synergistically. The multiple component framework is presented as Renewable Artificial Plant for In-situ Microbial Environmental Remediation (RAPIMER). RAPIMER exhibits high adsorption capacity for the PFAS compounds and diverse adsorption capability toward co-contaminants. Subsequently, RAPIMER provides the substrates and contaminants for in situ bioremediation via fungus Irpex lacteus and promotes PFAS detoxification. RAPIMER arises from cheap lignocellulosic sources, enabling a broader impact on sustainability and a means for low-cost pollutant remediation.