レプリケーション・プロテインAは、WASタンパク質と協力して、DNAの修復を助け、潜在的ながんの発生を予防している Replication protein A partners with the WAS protein to help repair DNA and prevent potential cancers from developing
2022-08-09 ペンシルベニア州立大学(PennState)
研究者らは、ウィスコット・アルドリッチ症候群(WAS)、すなわちWASpが欠損する遺伝性疾患の患者が、免疫系の機能を抑制しているだけでなく、場合によっては癌も発症していることを観察して、この発見をしたのである。
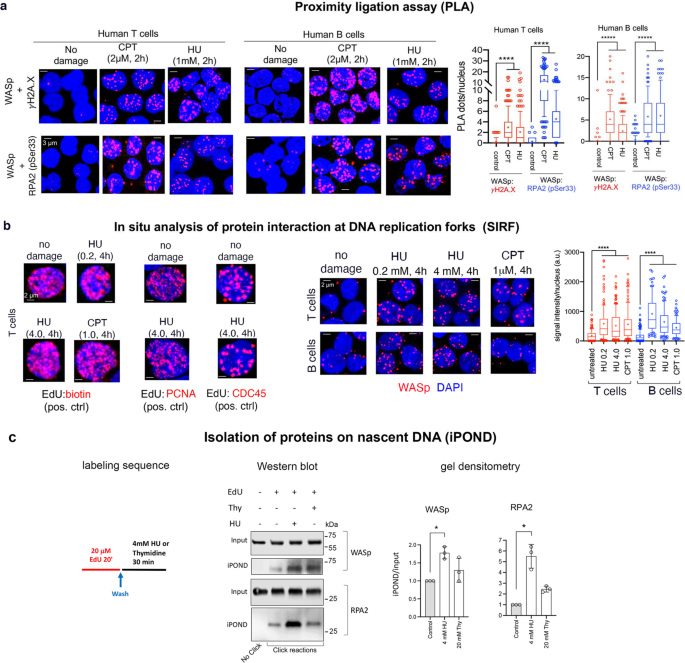
研究者達は、精製したヒトWASpとRPAを使ったタンパク質結合実験を行い、WASpがRPAと複合体を形成していることを発見しました。さらに、WASpがRPAを、DNAの一本鎖が切断されて修復が必要な部位に「誘導」していることも明らかになった。
この複合体がなければ、DNA修復は二次的なメカニズムで行われるため、癌につながる可能性がある。
<関連情報>
- https://www.psu.edu/news/research/story/it-takes-two-proteins-team-fix-damaged-dna-human-cells/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-022-31415-z
WASpは複製ストレスとDNA損傷に応答して、一本鎖DNA上のRPA機能を調節する(WASp modulates RPA function on single-stranded DNA in response to replication stress and DNA damage)
Seong-Su Han,Kuo-Kuang Wen,María L. García-Rubio,Marc S. Wold,Andrés Aguilera,Wojciech Niedzwiedz & Yatin M. Vyas
Nature Communications Published:29 June 2022
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-31415-z
Abstract
Perturbation in the replication-stress response (RSR) and DNA-damage response (DDR) causes genomic instability. Genomic instability occurs in Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome (WAS), a primary immunodeficiency disorder, yet the mechanism remains largely uncharacterized. Replication protein A (RPA), a single-strand DNA (ssDNA) binding protein, has key roles in the RSR and DDR. Here we show that human WAS-protein (WASp) modulates RPA functions at perturbed replication forks (RFs). Following genotoxic insult, WASp accumulates at RFs, associates with RPA, and promotes RPA:ssDNA complexation. WASp deficiency in human lymphocytes destabilizes RPA:ssDNA-complexes, impairs accumulation of RPA, ATR, ETAA1, and TOPBP1 at genotoxin-perturbed RFs, decreases CHK1 activation, and provokes global RF dysfunction. las17 (yeast WAS-homolog)-deficient S. cerevisiae also show decreased ScRPA accumulation at perturbed RFs, impaired DNA recombination, and increased frequency of DNA double-strand break (DSB)-induced single-strand annealing (SSA). Consequently, WASp (or Las17)-deficient cells show increased frequency of DSBs upon genotoxic insult. Our study reveals an evolutionarily conserved, essential role of WASp in the DNA stress-resolution pathway, such that WASp deficiency provokes RPA dysfunction-coupled genomic instability.


