2023-12-12 スイス連邦工科大学ローザンヌ校(EPFL)
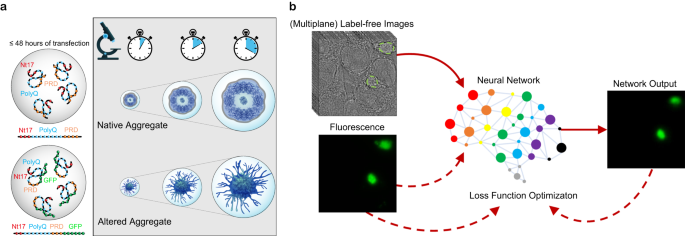
◆この手法はタンパク質の自然な状態を損なわず、高い忠実度のデータを提供するため、神経変性疾患の研究において革新的です。LINAはハンチントン病の文脈で高い精度でアグリゲートを同定し、ラベリングや蛍光の影響を受けないままでモニタリングできることが実証されました。将来的には他の神経変性疾患のタンパク質凝集体も対象にし、早期のイベントを捉え、新しい薬剤の開発につなげることが期待されます。
<関連情報>
- https://actu.epfl.ch/news/ai-unlocks-new-insights-in-neurodegenerative-disea/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-023-43440-7
ディープラーニングを用いたタンパク質凝集体のラベルフリー同定 Label-free identification of protein aggregates using deep learning
Khalid A. Ibrahim,Kristin S. Grußmayer,Nathan Riguet,Lely Feletti,Hilal A. Lashuel & Aleksandra Radenovic
Nature Communications Published:28 November 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-43440-7
Abstract
Protein misfolding and aggregation play central roles in the pathogenesis of various neurodegenerative diseases (NDDs), including Huntington’s disease, which is caused by a genetic mutation in exon 1 of the Huntingtin protein (Httex1). The fluorescent labels commonly used to visualize and monitor the dynamics of protein expression have been shown to alter the biophysical properties of proteins and the final ultrastructure, composition, and toxic properties of the formed aggregates. To overcome this limitation, we present a method for label-free identification of NDD-associated aggregates (LINA). Our approach utilizes deep learning to detect unlabeled and unaltered Httex1 aggregates in living cells from transmitted-light images, without the need for fluorescent labeling. Our models are robust across imaging conditions and on aggregates formed by different constructs of Httex1. LINA enables the dynamic identification of label-free aggregates and measurement of their dry mass and area changes during their growth process, offering high speed, specificity, and simplicity to analyze protein aggregation dynamics and obtain high-fidelity information.