新生児に起こる肺の病気は、特定のタンパク質の欠乏によって引き起こされることが判明し、この病気との闘いに貢献する可能性があります。 The fight against a devastating lung condition in newborn babies could be helped by the discovery that it is caused by a deficiency in a particular protein.
2022-08-29 エディンバラ大学
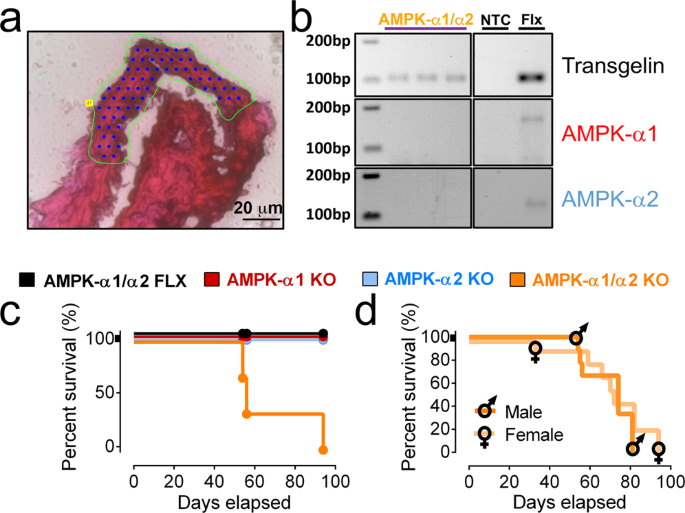
研究チームは、マウスを使った実験で、AMPKとPPHNとの関連を発見した。
研究チームは、10年にわたるマウスの研究で、平滑筋と呼ばれる血管を形成する1種類の細胞に遺伝子操作を行い、AMPK酵素を除去した。すべてのマウスは、出生後に特発性(原因不明の病気という意味)PPHNを発症し、12週齢までに死亡した。これは、人間の約5年分に相当する。
<関連情報>
- https://www.ed.ac.uk/news/2022/treatment-for-fatal-lung-disease-in-babies-closer
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-022-32568-7
平滑筋のAMPK欠損は新生児の遷延性肺高血圧症と早死を引き起こす AMPK deficiency in smooth muscles causes persistent pulmonary hypertension of the new-born and premature death
Javier Moral-Sanz,Sophronia A. Lewis,Sandy MacMillan,Marco Meloni,Heather McClafferty,Benoit Viollet,Marc Foretz,Jorge del-Pozo & A. Mark Evans
Nature Communications Published:26 August 2022
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-32568-7
Abstract
AMPK has been reported to facilitate hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction but, paradoxically, its deficiency precipitates pulmonary hypertension. Here we show that AMPK-α1/α2 deficiency in smooth muscles promotes persistent pulmonary hypertension of the new-born. Accordingly, dual AMPK-α1/α2 deletion in smooth muscles causes premature death of mice after birth, associated with increased muscularisation and remodeling throughout the pulmonary arterial tree, reduced alveolar numbers and alveolar membrane thickening, but with no oedema. Spectral Doppler ultrasound indicates pulmonary hypertension and attenuated hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction. Age-dependent right ventricular pressure elevation, dilation and reduced cardiac output was also evident. KV1.5 potassium currents of pulmonary arterial myocytes were markedly smaller under normoxia, which is known to facilitate pulmonary hypertension. Mitochondrial fragmentation and reactive oxygen species accumulation was also evident. Importantly, there was no evidence of systemic vasculopathy or hypertension in these mice. Moreover, hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction was attenuated by AMPK-α1 or AMPK-α2 deletion without triggering pulmonary hypertension.