2022-09-28 スイス連邦工科大学ローザンヌ校(EPFL)
膨大なデータの必要性を回避しながら、実験的な観察や測定に対応するモデルを作成できるとしたらどうでしょう?
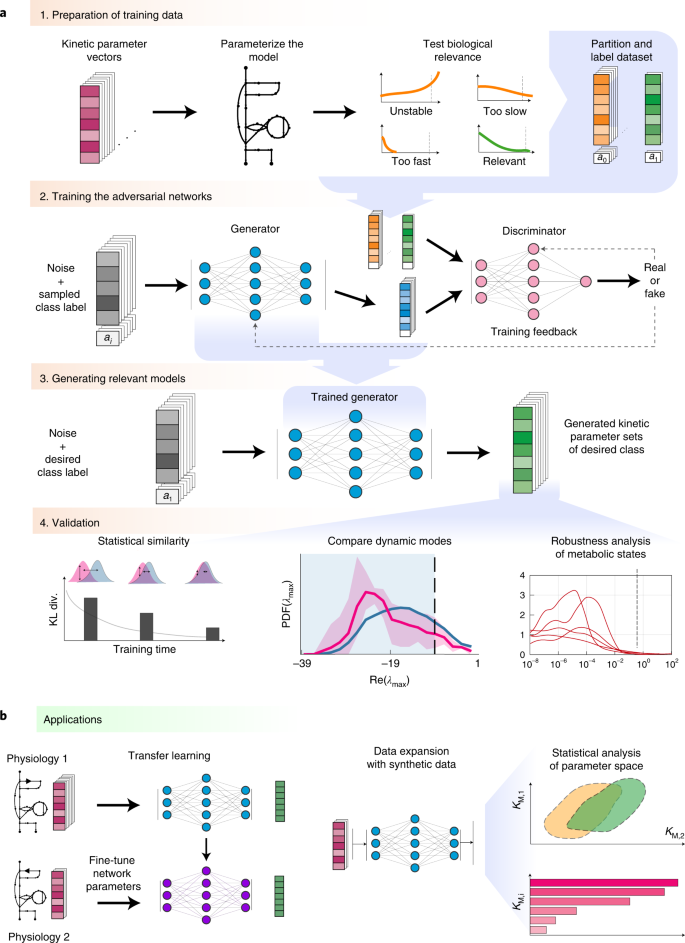
EPFLの科学者たちは、細胞で観察される動的な代謝特性を再現するディープラーニングベースの計算フレームワーク「REKINDLE」でまさにそれを提案している。
REKINDLEによって、研究コミュニティは、運動学的モデルを生成するための計算量を数桁削減することができるようになり、これらのモデルに生化学的データを統合することで、新しい仮説を立て、実験的観察を解明し、新しい治療法の発見やバイオテクノロジーの設計に役立てることができる。
<関連情報>
- https://actu.epfl.ch/news/better-understanding-of-cellular-metabolism-with-t/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s42256-022-00519-y
敵対的生成ネットワークを用いた代謝の動力学的研究のための動力学モデルの再構築. Reconstructing Kinetic Models for Dynamical Studies of Metabolism using Generative Adversarial Networks
Subham Choudhury,Michael Moret,Pierre Salvy,Daniel Weilandt,Vassily Hatzimanikatis & Ljubisa Miskovic
Nature Machine Intelligence Published:DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s42256-022-00519-y
Abstract
Kinetic models of metabolism relate metabolic fluxes, metabolite concentrations and enzyme levels through mechanistic relations, rendering them essential for understanding, predicting and optimizing the behaviour of living organisms. However, due to the lack of kinetic data, traditional kinetic modelling often yields only a few or no kinetic models with desirable dynamical properties, making the analysis unreliable and computationally inefficient. We present REKINDLE (Reconstruction of Kinetic Models using Deep Learning), a deep-learning-based framework for efficiently generating kinetic models with dynamic properties matching the ones observed in cells. We showcase REKINDLE’s capabilities to navigate through the physiological states of metabolism using small numbers of data with significantly lower computational requirements. The results show that data-driven neural networks assimilate implicit kinetic knowledge and structure of metabolic networks and generate kinetic models with tailored properties and statistical diversity. We anticipate that our framework will advance our understanding of metabolism and accelerate future research in biotechnology and health.