2022-12-12 ペンシルベニア州立大学(PennState)

研究者によると、この研究結果は生産苗床や森林管理者が在庫を保護するための管理上の決断を下すのに役立つという。
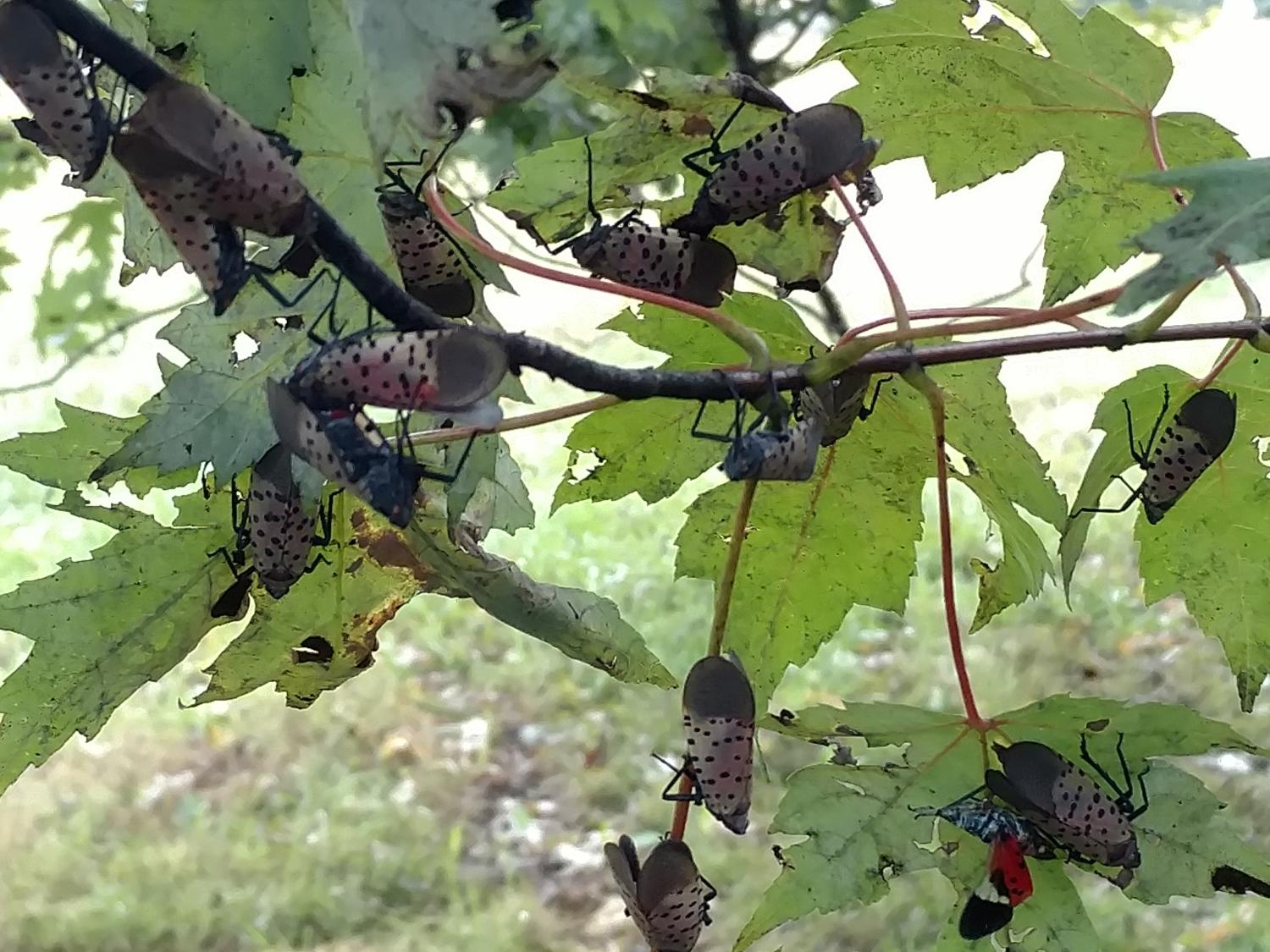
アジアを起源とするこのウンカは、2014年にバークス郡で米国で初めて発見され、その後、ペンシルベニア州の45郡と周辺の州に広がっています。この害虫は、突き刺すように吸引する口器で100種以上の植物の樹液を食べ、同じく外来種であるツリーオブヘブンや野生・栽培ブドウを強く好むとされています。
<関連情報>
- https://www.psu.edu/news/agricultural-sciences/story/study-examines-feeding-damage-caused-spotted-lanternflies-young-maples/
- https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/finsc.2022.1080124/full
広葉樹若木の生態系に及ぼすハダニ類による短期摂食の影響
Impacts of short-term feeding by spotted lanternfly (Lycorma delicatula) on ecophysiology of young hardwood trees in a common garden
Emily Lavely, Lidiia Iavorivska, Osariyekemwen Uyi, David M. Eissenstat, Brian Walsh, Edward J. Primka IV, Jeremy Harper and Kelli Hoover
Frontiers of Insect Science Published:07 December 2022
DOI:https://doi.org/10.3389/finsc.2022.1080124
Spotted lanternfly (SLF; Lycorma delicatula White; Hemiptera: Fulgoridae) invaded the US from Asia and was first detected in 2014; currently, populations have established in 14 states primarily in the Northeast and Mid-Atlantic. It feeds voraciously on phloem sap from a broad range of host plants, with a preference for tree of heaven (Ailanthus altissima [Sapindales: Simaroubaceae]), grapevines (Vitis spp. [Vitales: Vitaceae]), and several common hardwood tree species. We evaluated the impacts of fourth instars and adults confined to a single branch or whole trees on gas exchange attributes (carbon assimilation [photosynthetic rate], transpiration and stomatal conductance), selected nutrients, and diameter growth using young saplings of four host tree species planted in a common garden. In general, the effects of adults on trees were greater than nymphs, although there was variation depending on tree species, pest density, and time post-infestation. Nymphs on a single branch of red maple (Acer rubrum [Sapindales: Sapindaceae]), or silver maple (Acer saccharinum [Sapindales: Sapindaceae]) at three densities (0, 15, or 30) had no significant effects on gas exchange. In contrast, 40 adults confined to a single branch of red or silver maple rapidly suppressed gas exchange and reduced nitrogen concentration in leaves; soluble sugars in branch wood were reduced in the fall for silver maple and in the following spring for red maple. Fourth instars confined to whole silver maple trees reduced soluble sugars in leaves and branch wood, and reduced tree diameter growth by >50% during the next growing season. In contrast, fourth instars in whole tree enclosures had no effects on black walnut (Juglans nigra [Fagales: Juglandaceae]). SLF enclosed on tree of heaven at 80 adults per tree suppressed gas exchange after two weeks of feeding, but did not alter non-structural carbohydrates, nitrogen concentrations, or tree growth. Results suggest that moderate to heavy feeding by SLF on young maple saplings may impair tree growth, which could have implications for production nurseries and forest managers.