2023-01-16 スウェーデン・リンショーピング大学
ピーター・ニルソンがトレーサー分子の研究を始めた当時、トレーサー分子は小さな化学部品から構成されており、それがポリマーと呼ばれる長い鎖を形成していた。それ以来、研究者たちはトレーサー分子を分子レベルの精度で再構築し、原子の一つひとつの位置を正確に把握できるようになった。
トレーサー分子は、特定のタンパク質を認識する能力があるため、世界中の研究者に役立っています。トレーサー分子が標的タンパク質を見つけると、それに結合し、その曲げやすい背骨のおかげで、そのタンパク質に合わせて型をとることができるのです。巧妙なのは、研究者がトレーサー分子に光を当てると、分子が光り返してくることだ。この現象は蛍光と呼ばれています。背骨のねじれによって、分子はさまざまな色を放つことができるのです。このおかげで、研究者は有害なタンパク質の凝集体の形状を調べることができ、アルツハイマー病やその他の認知症を理解する鍵となる可能性があるのです。
研究グループは現在、アルツハイマー病に見られる凝集体にのみ結合し、密接に関連する疾患の類似プラークには結合しないトレーサー分子の開発に着手している。これにより、トレーサー分子をヒトに用いて、有害なタンパク質の凝集体を発見し、具体的な診断を下す可能性が出てきた。
ここ数年、研究者たちは、トレーサー分子が治療にも使える可能性があることを見出している。EMBO Molecular medicine』誌に最近掲載された研究では、アルツハイマー病のマウスを用いて、アミロイドβタンパク質のミスフォールド変異体が集合して脳垢が形成されることを明らかにした。ミスフォールドしたタンパク質は、正常な変異体も有害な形態に変化させ、タンパク質の凝集体の量を増加させることがある。チューリッヒ大学の研究者が主導した今回の研究では、LiU研究者のトレーサー分子を投与されたマウスでは、アミロイド斑の量が減少していた。研究者らは、トレーサー分子が有害なタンパク質凝集体に結合することで、運命的な連鎖反応がブロックされると考えています。
<関連情報>
- https://liu.se/en/news-item/peter-nilssons-molekyler-lyser-upp-alzheimerforskningen
- https://www.embopress.org/doi/full/10.15252/emmm.202216789
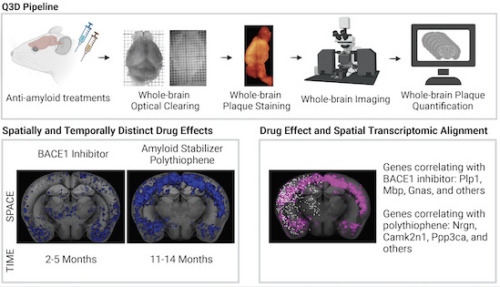
全脳顕微鏡観察により、抗Aβ療法が時間的・空間的に異なる効果を示すことが明らかになった Whole-brain microscopy reveals distinct temporal and spatial efficacy of anti-Aβ therapies
Daniel KirschenbaumEhsan Dadgar-KianiFrancesca CattoFabian F VoigtChiara TrevisanOliver BichselHamid ShiraniK Peter R NilssonKarl J FrontzekPaolo PaganettiFritjof HelmchenJin Hyung LeeAdriano Aguzzi
EMBO Molecular Medicine Published:16 November 2022
DOI:https://doi.org/10.15252/emmm.202216789
Abstract
Many efforts targeting amyloid-β (Aβ) plaques for the treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease thus far have resulted in failures during clinical trials. Regional and temporal heterogeneity of efficacy and dependence on plaque maturity may have contributed to these disappointing outcomes. In this study, we mapped the regional and temporal specificity of various anti-Aβ treatments through high-resolution light-sheet imaging of electrophoretically cleared brains. We assessed the effect on amyloid plaque formation and growth in Thy1-APP/PS1 mice subjected to β-secretase inhibitors, polythiophenes, or anti-Aβ antibodies. Each treatment showed unique spatiotemporal Aβ clearance, with polythiophenes emerging as a potent anti-Aβ compound. Furthermore, aligning with a spatial-transcriptomic atlas revealed transcripts that correlate with the efficacy of each Aβ therapy. As observed in this study, there is a striking dependence of specific treatments on the location and maturity of Aβ plaques. This may also contribute to the clinical trial failures of Aβ-therapies, suggesting that combinatorial regimens may be significantly more effective in clearing amyloid deposition.