2023-02-22 デラウェア大学 (UD)
◆この発見は、運動学・応用生理学の助教授でデラウェア州認知加齢研究センター所長のクリストファー・マーテンスと、国立加齢研究所の上級研究員ディミトリオス・カポジアニス博士によってなされたものです。この発見は、NRが脳に到達すると、アルツハイマー病などの神経変性疾患に関連する生物学的経路の代謝を変化させることができるという考えを裏付けるものであり、重要なものです。この研究成果は、NIHの助成金およびNIH National Institute on AgingのIntramural Research Programの一部によって支援され、最近、雑誌『Aging Cell』に発表されました。
◆NRは、摂取すると容易にニコチンアミドアデニンジヌクレオチド(NAD+)に変換され、細胞修復や損傷したDNAの修復に不可欠な物質です。
◆”NAD+は、年をとったり慢性疾患を発症したりすると、徐々に失われていきます。NAD+の損失は、肥満や喫煙などのネガティブな生活習慣と関連しています」とマーテンスは述べています。”それらの負の結果を打ち消すためには、より多くのNAD+が必要なので、負の生活習慣に直面すると、より枯渇しやすくなるのです。”
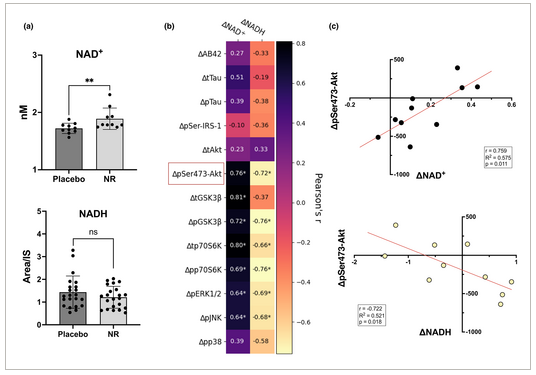
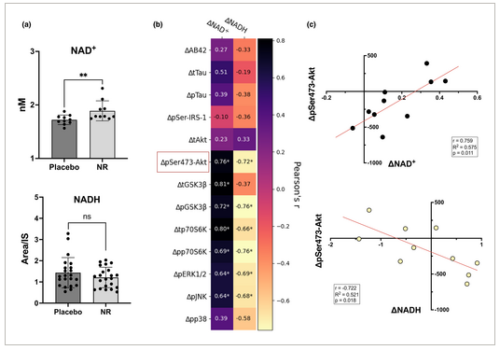
◆研究者らは、最初の初期臨床試験のサンプルを用いて、まず、6週間後にこれらの小胞内でNAD+レベルが上昇することを確認した。
◆マーテンスとカポギアニスは、これらの神経変性バイオマーカーとNAD+の変化との間に相関関係があることも発見しました。
◆これらの血液ベースのバイオマーカーのいくつかは、NAD+の枯渇が、アルツハイマー病や他の神経変性疾患の原因であるかどうかを判断するために、将来的に使われるかもしれません。この種の検査が、より日常的な検査として、一般の人々にも利用できるようになる可能性さえあるのです。
◆マーテンスとカポギアニスは、その有効性を証明した後、NRの使用量を増やすことで認知機能が改善されるかどうか、そして、最終的には、神経変性疾患の進行を遅らせるために使用できるかどうかを検証する予定です。
<関連情報>
- https://www.udel.edu/udaily/2023/february/alzheimers-research-delaware-center-for-cognitive-aging/
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/acel.13754#.Y5nVITl-nME.twitter
ニコチンアミドリボシドの経口投与によりNAD+が上昇し、神経細胞由来に富む血漿細胞外小胞の神経変性病態のバイオマーカーを低下させる Oral nicotinamide riboside raises NAD+ and lowers biomarkers of neurodegenerative pathology in plasma extracellular vesicles enriched for neuronal origin
Michael Vreones, Maja Mustapic, Ruin Moaddel, Krishna A. Pucha, Jacqueline Lovett, Douglas R. Seals, Dimitrios Kapogiannis, Christopher R. Martens
Aging Cell Published: 14 December 2022
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.13754
Abstract
Declining nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) concentration in the brain during aging contributes to metabolic and cellular dysfunction and is implicated in the pathogenesis of aging-associated neurological disorders. Experimental therapies aimed at boosting brain NAD+ levels normalize several neurodegenerative phenotypes in animal models, motivating their clinical translation. Dietary intake of NAD+ precursors, such as nicotinamide riboside (NR), is a safe and effective avenue for augmenting NAD+ levels in peripheral tissues in humans, yet evidence supporting their ability to raise NAD+ levels in the brain or engage neurodegenerative disease pathways is lacking. Here, we studied biomarkers in plasma extracellular vesicles enriched for neuronal origin (NEVs) from 22 healthy older adults who participated in a randomized, placebo-controlled crossover trial (NCT02921659) of oral NR supplementation (500 mg, 2x /day, 6 weeks). We demonstrate that oral NR supplementation increases NAD+ levels in NEVs and decreases NEV levels of Aβ42, pJNK, and pERK1/2 (kinases involved in insulin resistance and neuroinflammatory pathways). In addition, changes in NAD(H) correlated with changes in canonical insulin–Akt signaling proteins and changes in pERK1/2 and pJNK. These findings support the ability of orally administered NR to augment neuronal NAD+ levels and modify biomarkers related to neurodegenerative pathology in humans. Furthermore, NEVs offer a new blood-based window into monitoring the physiologic response of NR in the brain.