2023-05-18 チャルマース工科大学
◆最近の都市では道路と住宅の距離が縮まり、健康と仕事に悪影響を及ぼす問題が深刻化している。規制は平均騒音を考慮し、低周波のピークや室内騒音は対象外。
◆研究者は、室内のノイズ環境を改善するための調整や都市密集を避けることが重要と述べている。
<関連情報>
- https://news.cision.com/chalmers/r/even-weak-traffic-noise-has-a-negative-impact-on-work-performance,c3771593
- https://www.mdpi.com/1660-4601/20/5/3798
- https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/1351010X221143571
中程度のレベルの交通騒音は認知能力に影響を与える: 距離による時間的変化は重要か? Traffic Noise at Moderate Levels Affects Cognitive Performance: Do Distance-Induced Temporal Changes Matter?
Leon Müller,Jens Forssén and Wolfgang Kropp
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health Published: 21 February 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20053798
Abstract
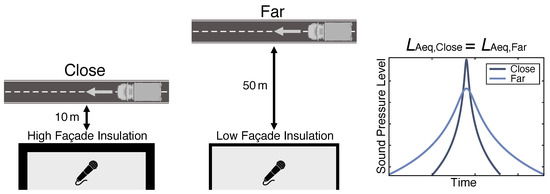
Urbanization leads to an increased demand for urban housing, which can be met by building dwellings closer to streets. Regulations often limit equivalent sound pressure levels which do not account for changes in time structure that occur when decreasing the road distance. This study investigates the effect of such temporal changes on subjective workload and cognitive performance. A group of 42 participants performed a continuous performance test as well as a NASA-TLX workload test under three different sound conditions, i.e., close traffic, far traffic, both with the same equivalent sound pressure level of LAeq≈40dB, and silence. Additionally, participants answered a questionnaire regarding their preferred acoustic environment for concentrated working. Significant effects of the sound condition on the multivariate workload results as well as on the number of commission errors in the continuous performance test were found. Post hoc tests showed no significant differences between the two noise conditions, but there were significant differences between noise and silence. This indicates that moderate traffic noise levels can influence cognitive performance and perceived workload. If there is a difference in the human response to road traffic noise with constant LAeq but different time structures, the used methods are not suitable to detect them.
道路交通に起因する屋内低周波騒音暴露のモデル研究 A model study of low-frequency noise exposure indoors due to road traffic
Jens Forssén, Georgios Zachos, Carmen Rosas Perez and Wolfgang Kropp
Building Acoustics Published:January 11, 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1177/1351010X221143571

Abstract
Indoor low-frequency noise levels due to road traffic has been modelled for facade examples consisting of a lightweight steel facade, a concrete facade and two types of windows. Possible audibility of heavy vehicles passing by has been investigated as well as the dependence of the exposure level on driving speed and distance to road. The results show that pass-by events may be audible at low frequencies for cases complying with building standards and noise guideline values exemplified by Swedish regulation. Moreover, the A-weighted levels may be dominated by low frequency noise, and the frequency of occurrence of pass-by traffic noise events may be sufficiently high to create disturbance for typical traffic situations. Furthermore, it is shown that the contribution of pass-by events to the equivalent level indoors may increase when the driving speed is lowered.

