2023-05-31 ペンシルベニア州立大学(PennState)
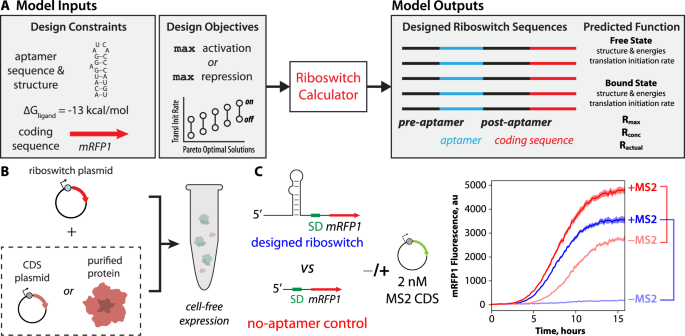
◆研究チームは、無細胞発現システムとリボスイッチと呼ばれる人工RNAベースのセンサーを組み合わせて、バイオマーカー・タンパク質を検出しました。リボスイッチは、特定のタンパク質に結合し、観測可能なシグナルを制御するように設計されている。研究チームは、計算機設計を応用して、凍結乾燥と再水和が可能な低コストのタンパク質センサーを設計した。
◆次のステップは、広く使用するための使いやすいデバイスを開発することです。本研究は、国防高等研究計画局および空軍科学研究局の支援を受けて行われました。
<関連情報>
- https://www.psu.edu/news/engineering/story/penn-state-engineers-report-low-cost-human-biomarker-sensor-designs/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-023-38098-0
無細胞発現系でヒトバイオマーカーを検出するタンパク質結合型リボスイッチの自動設計を実現 Automated design of protein-binding riboswitches for sensing human biomarkers in a cell-free expression system
Grace E. Vezeau,Lipika R. Gadila & Howard M. Salis
Nature Communications Published:27 April 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-38098-0
Abstract
Cell-free genetically encoded biosensors have been developed to detect small molecules and nucleic acids, but they have yet to be reliably engineered to detect proteins. Here we develop an automated platform to convert protein-binding RNA aptamers into riboswitch sensors that operate within low-cost cell-free assays. We demonstrate the platform by engineering 35 protein-sensing riboswitches for human monomeric C-reactive protein, human interleukin-32γ, and phage MS2 coat protein. The riboswitch sensors regulate output expression levels by up to 16-fold with input protein concentrations within the human serum range. We identify two distinct mechanisms governing riboswitch-mediated regulation of translation rates and leverage computational analysis to refine the protein-binding aptamer regions, improving design accuracy. Overall, we expand the cell-free sensor toolbox and demonstrate how computational design is used to develop protein-sensing riboswitches with future applications as low-cost medical diagnostics.


