2023-06-14 ニューサウスウェールズ大学(UNSW)
◆海綿を3℃上昇させると、1つの重要な微生物が海綿から離れ、組織中毒を引き起こす可能性があることが明らかになった。気候変動が海綿の生態系に与える影響について、この研究が重要な一片を提供している。
<関連情報>
- https://newsroom.unsw.edu.au/news/science-tech/marine-mystery-finding-link-between-climate-change-and-sea-sponge-loss
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s43705-023-00247-3
将来の海洋環境は、海綿の壊死、微生物異常、栄養循環のアンバランスを誘発する。 Future ocean conditions induce necrosis, microbial dysbiosis and nutrient cycling imbalance in the reef sponge Stylissa flabelliformis
Emmanuelle S. Botté,Holly Bennett,J. Pamela Engelberts,Torsten Thomas,James J. Bell,Nicole S. Webster & Heidi M. Luter
ISME Communications Published:14 June 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s43705-023-00247-3
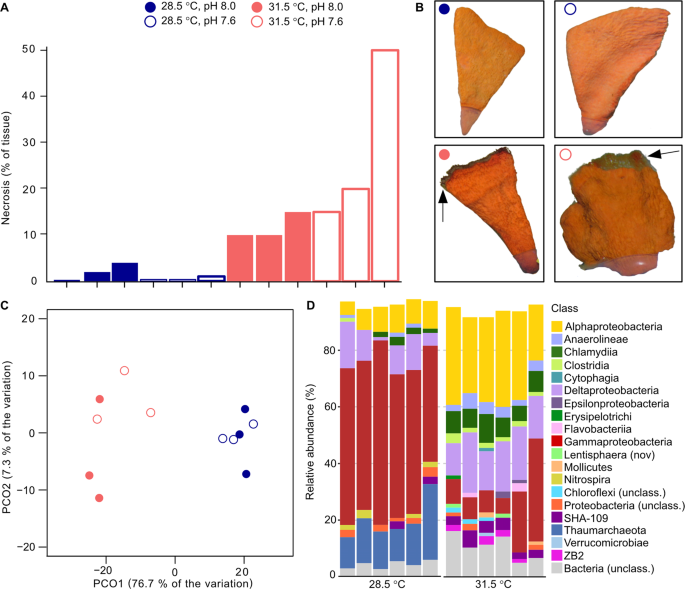
Abstract
Oceans are rapidly warming and acidifying in the context of climate change, threatening sensitive marine biota including coral reef sponges. Ocean warming (OW) and ocean acidification (OA) can impact host health and associated microbiome, but few studies have investigated these effects, which are generally studied in isolation, on a specific component of the holobiont. Here we present a comprehensive view of the consequences of simultaneous OW and OA for the tropical sponge Stylissa flabelliformis. We found no interactive effect on the host health or microbiome. Furthermore, OA (pH 7.6 versus pH 8.0) had no impact, while OW (31.5 °C versus 28.5 °C) caused tissue necrosis, as well as dysbiosis and shifts in microbial functions in healthy tissue of necrotic sponges. Major taxonomic shifts included a complete loss of archaea, reduced proportions of Gammaproteobacteria and elevated relative abundances of Alphaproteobacteria. OW weakened sponge-microbe interactions, with a reduced capacity for nutrient exchange and phagocytosis evasion, indicating lower representations of stable symbionts. The potential for microbially-driven nitrogen and sulphur cycling was reduced, as was amino acid metabolism. Crucially, the dysbiosis annihilated the potential for ammonia detoxification, possibly leading to accumulation of toxic ammonia, nutrient imbalance, and host tissue necrosis. Putative defence against reactive oxygen species was greater at 31.5 °C, perhaps as microorganisms capable of resisting temperature-driven oxidative stress were favoured. We conclude that healthy symbiosis in S. flabelliformis is unlikely to be disrupted by future OA but will be deeply impacted by temperatures predicted for 2100 under a “business-as-usual” carbon emission scenario.