2023-12-22 カロリンスカ研究所(KI)
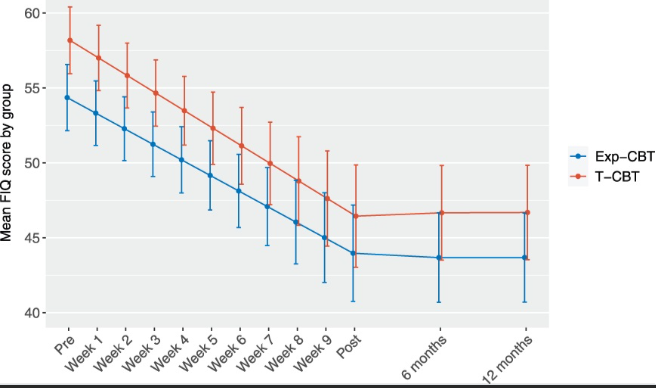
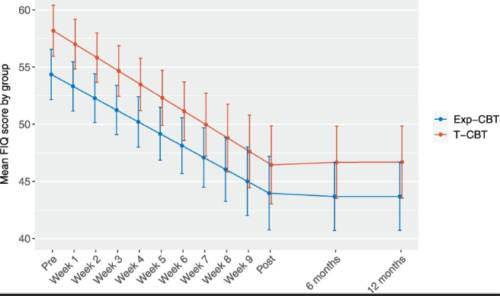
◆スウェーデンでは20万人がこの慢性疼痛症候群に苦しむが、既存薬の効果が不十分であり、CBTは効果があるものの実践者不足と効果的な形態の不明確さが課題だ。研究は274人の患者を対象に、オンラインでの伝統的CBTと暴露ベースCBTを比較。どちらも症状の有意な軽減を示し、オンライン治療がファイブロマイアルギア患者に有益である可能性を示唆している。
<関連情報>
- https://news.ki.se/two-types-of-cbt-are-equally-effective-in-the-treatment-of-fibromyalgia
- https://journals.lww.com/pain/fulltext/9900/effect_of_exposure_based_vs_traditional_cognitive.475.aspx
線維筋痛症に対する曝露ベースの認知行動療法と従来の認知行動療法の効果:2施設単盲検ランダム化比較試験 Effect of exposure-based vs traditional cognitive behavior therapy for fibromyalgia: a two-site single-blind randomized controlled trial
Hedman-Lagerlöf, Maria; Gasslander, Nils; Ahnlund Hoffmann, Alice; Bragesjö, Maria; Etzell, Amanda; Ezra, Simon; Frostell, Elsa; Hedman-Lagerlöf, Erik; Ivert, Caroline; Liliequist, Björn; Ljótsson, Brjánn; Hoppe, Johanna M.; Palmgren, Josefin; Spansk, Edward; Sundström, Felicia; Särnholm, Josefin; Tzavara, Georgia; Buhrman, Monica; Axelsson, Erland
PAIN Published:December 22, 2023
DOI: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000003128
Abstract
Fibromyalgia is a debilitating pain condition for which treatment effects are typically modest. The most evaluated psychological treatment is traditional cognitive behavior therapy (T-CBT), but promising effects have recently been seen in exposure-based cognitive behavior therapy (Exp-CBT). We investigated whether Exp-CBT was superior to T-CBT in a randomized controlled trial. Self-referred participants with fibromyalgia (N = 274) were randomized (1:1) to 10 weeks of Exp-CBT or T-CBT. Treatments were delivered online and presented as “CBT for fibromyalgia.” Participants were assessed at baseline, weekly during treatment, posttreatment, and at 6- and 12-month follow-up. Primary outcome was the difference in reduction in fibromyalgia severity as measured using the Fibromyalgia Impact Questionnaire (FIQ) over 11 assessment points from baseline to posttreatment, modelled within an intention-to-treat framework using linear mixed effects models fitted on multiple imputed data. Approximately 91% of weekly FIQ scores were collected over the main phase. There was no significant difference between Exp-CBT and T-CBT in the mean reduction of fibromyalgia severity from pretreatment to posttreatment (b = 1.3, 95% CI -3.0 to 5.7, P = 0.544, d = -0.10). Minimal clinically important improvement was seen 60% in Exp-CBT vs 59% in T-CBT. Effects were sustained up to 12 months posttreatment. This well-powered randomized trial indicated that Exp-CBT was not superior to T-CBT for fibromyalgia. Both treatments were associated with a marked reduction in fibromyalgia severity, and the online treatment format might be of high clinical utility. T-CBT can still be regarded a reference standard treatment that remains clinically relevant when compared to novel treatment approaches.