2024-02-05 マサチューセッツ工科大学(MIT)
◆AIアルゴリズムの支援が医師の正確性を向上させることが示されたが、その効果は薄い肌の患者の診断でより大きかった。これは、皮膚診断における医師の診断格差を初めて示した研究であり、教科書やトレーニング資料の画像が主に薄い肌であることが原因の一つと考えられている。
<関連情報>
- https://news.mit.edu/2024/doctors-more-difficulty-diagnosing-diseases-images-darker-skin-0205
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-023-02728-3
ディープラーニングによる肌色を超えた皮膚疾患診断の意思決定支援 Deep learning-aided decision support for diagnosis of skin disease across skin tones
Matthew Groh,Omar Badri,Roxana Daneshjou,Arash Koochek,Caleb Harris,Luis R. Soenksen,P. Murali Doraiswamy & Rosalind Picard
Nature Medicine Published:05 February 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-023-02728-3
Abstract
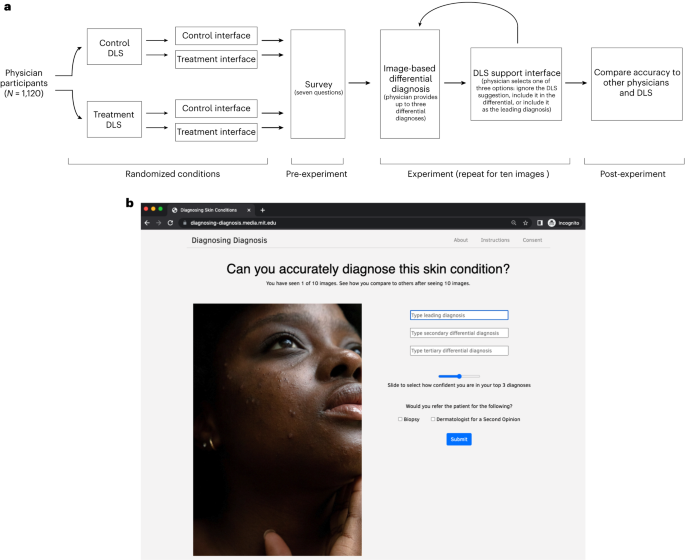
Although advances in deep learning systems for image-based medical diagnosis demonstrate their potential to augment clinical decision-making, the effectiveness of physician–machine partnerships remains an open question, in part because physicians and algorithms are both susceptible to systematic errors, especially for diagnosis of underrepresented populations. Here we present results from a large-scale digital experiment involving board-certified dermatologists (n = 389) and primary-care physicians (n = 459) from 39 countries to evaluate the accuracy of diagnoses submitted by physicians in a store-and-forward teledermatology simulation. In this experiment, physicians were presented with 364 images spanning 46 skin diseases and asked to submit up to four differential diagnoses. Specialists and generalists achieved diagnostic accuracies of 38% and 19%, respectively, but both specialists and generalists were four percentage points less accurate for the diagnosis of images of dark skin as compared to light skin. Fair deep learning system decision support improved the diagnostic accuracy of both specialists and generalists by more than 33%, but exacerbated the gap in the diagnostic accuracy of generalists across skin tones. These results demonstrate that well-designed physician–machine partnerships can enhance the diagnostic accuracy of physicians, illustrating that success in improving overall diagnostic accuracy does not necessarily address bias.