2024-05-03 カリフォルニア大学サンタバーバラ校(UCSB)
<関連情報>
- https://news.ucsb.edu/2024/021464/researchers-find-new-mothers-immune-status-varies-her-feeding-strategy
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-024-54963-4
母親の授乳方法のばらつきが母親の日内炎症の変化と関連していることが判明 Variation in maternal lactation practices associated with changes in diurnal maternal inflammation
Carmen Hove,Kristine Joy Chua,Melanie Ann Martin,Madison Hubble & Amy M. Boddy
Scientific Reports Published:22 February 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-54963-4
Abstract
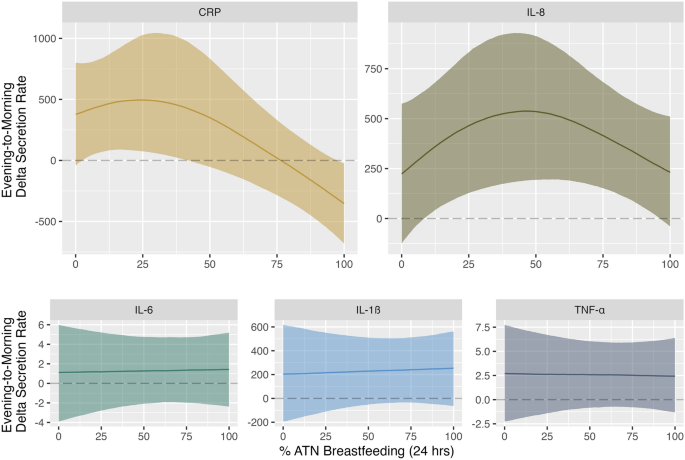
While the importance of human milk in shaping infant immune function is well established, the impact of at-the-nipple (ATN) breastfeeding on maternal immune status has been understudied. Since lactation evolved to support infant survival and boost maternal fitness, we predict that ATN breastfeeding will confer benefits on maternal immune function. We measure the absolute and relative frequency of different infant feeding methods (ATN breastfeeding, pumping, donated milk, other supplementation) used by postpartum women in Seattle, WA (USA). We implement Bayesian modeling to estimate the effects of ATN breastfeeding on diurnal change in secretion rate of “pro-inflammatory” salivary cytokines and C-reactive protein (CRP). Our results show that most mothers in our sample used a variety of infant feeding methods, with pumping as the most common alternative to ATN breastfeeding. We find that ATN breastfeeding is associated with non-linear effects on diurnal IL-8 and CRP. Furthermore, we find that women who report zero versus ubiquitous ATN breastfeeding exhibit opposing diurnal patterns in CRP secretion rate. This study provides evidence that variation in maternal lactation practices corresponds to differences in maternal immune responses, highlighting how measuring lactation as a continuous variable can further enhance understanding of postpartum maternal physiology.