2024-05-07 ワシントン大学セントルイス校
<関連情報>
- https://source.wustl.edu/2024/05/some-brain-tumors-may-be-linked-to-head-injury-mouse-study-suggests/
- https://actaneurocomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s40478-024-01735-w
脳損傷は神経細胞-グリアシグナル伝達を介して視神経膠腫形成を促進する Brain injury drives optic glioma formation through neuron-glia signaling
Jit Chatterjee,Joshua P. Koleske,Astoria Chao,Andrew D. Sauerbeck,Ji-Kang Chen,Xuanhe Qi,Megan Ouyang,Lucy G. Boggs,Rujuta Idate,Lara Isabel Marco Y Marquez,Terrence T. Kummer & David H. Gutmann
Acta Neuropathologica Communications Published:02 February 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1186/s40478-024-01735-w
Abstract
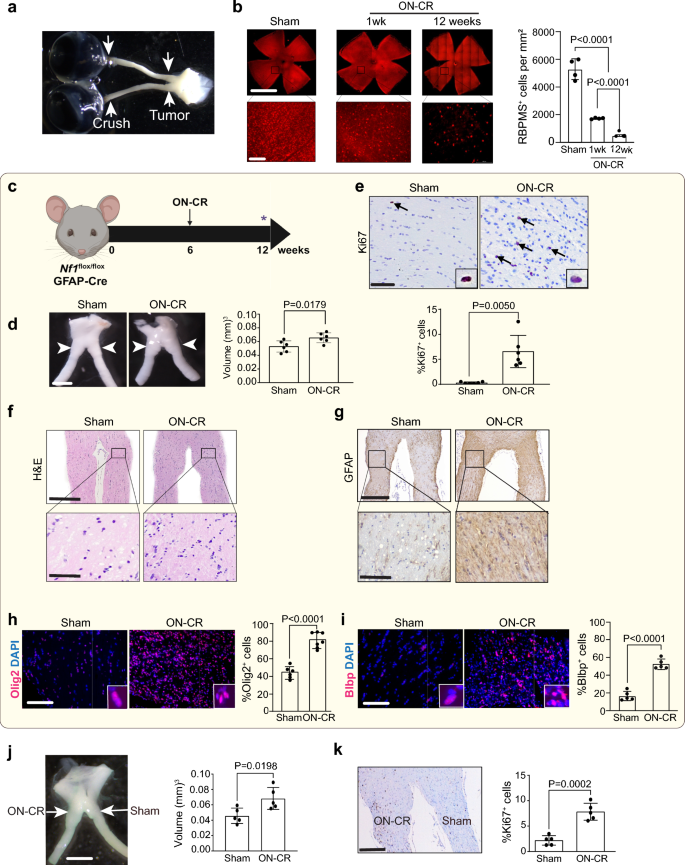
Tissue injury and tumorigenesis share many cellular and molecular features, including immune cell (T cells, monocytes) infiltration and inflammatory factor (cytokines, chemokines) elaboration. Their common pathobiology raises the intriguing possibility that brain injury could create a tissue microenvironment permissive for tumor formation. Leveraging several murine models of the Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) cancer predisposition syndrome and two experimental methods of brain injury, we demonstrate that both optic nerve crush and diffuse traumatic brain injury induce optic glioma (OPG) formation in mice harboring Nf1-deficient preneoplastic progenitors. We further elucidate the underlying molecular and cellular mechanisms, whereby glutamate released from damaged neurons stimulates IL-1β release by oligodendrocytes to induce microglia expression of Ccl5, a growth factor critical for Nf1-OPG formation. Interruption of this cellular circuit using glutamate receptor, IL-1β or Ccl5 inhibitors abrogates injury-induced glioma progression, thus establishing a causative relationship between injury and tumorigenesis.