2024-05-10 マサチューセッツ工科大学(MIT)
<関連情報>
- https://news.mit.edu/2024/using-mri-engineers-have-found-way-detect-light-deep-brain-0510
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41551-024-01210-w
光増感された血管系から局所的な血流力学的コントラストを検出することによる生物発光のイメージング Imaging bioluminescence by detecting localized haemodynamic contrast from photosensitized vasculature
Robert Ohlendorf,Nan Li,Valerie Doan Phi Van,Miriam Schwalm,Yuting Ke,Miranda Dawson,Ying Jiang,Sayani Das,Brenna Stallings,Wen Ting Zheng & Alan Jasanoff
Nature Biomedical Engineering Published:10 May 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41551-024-01210-w
Abstract
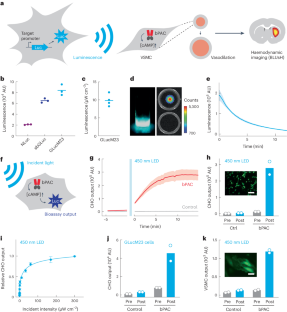
Bioluminescent probes are widely used to monitor biomedically relevant processes and cellular targets in living animals. However, the absorption and scattering of visible light by tissue drastically limit the depth and resolution of the detection of luminescence. Here we show that bioluminescent sources can be detected with magnetic resonance imaging by leveraging the light-mediated activation of vascular cells expressing a photosensitive bacterial enzyme that causes the conversion of bioluminescent emission into local changes in haemodynamic contrast. In the brains of rats with photosensitized vasculature, we used magnetic resonance imaging to volumetrically map bioluminescent xenografts and cell populations virally transduced to express luciferase. Detecting bioluminescence-induced haemodynamic signals from photosensitized vasculature will extend the applications of bioluminescent probes.