2024-06-10 ペンシルベニア州立大学(PennState)
<関連情報>
- https://www.psu.edu/news/health-and-human-development/story/does-beet-day-keep-heart-disease-away/
- https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2024.1359671/full
7日間の硝酸塩補給は閉経後女性の基礎大血管機能を臨床的に有意に改善する:無作為プラセボ対照二重盲検クロスオーバー臨床試験
Seven-day dietary nitrate supplementation clinically significantly improves basal macrovascular function in postmenopausal women: a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, crossover clinical trial
Jocelyn M. Delgado Spicuzza,Jigar Gosalia,Liezhou Zhong,Catherine Bondonno,Kristina S. Petersen,Mary Jane De Souza,Elmira Alipour,Daniel B. Kim-Shapiro,Yasina B. Somani,David N. Proctor
Frontiers in Nutrition Published:10 June 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2024.1359671
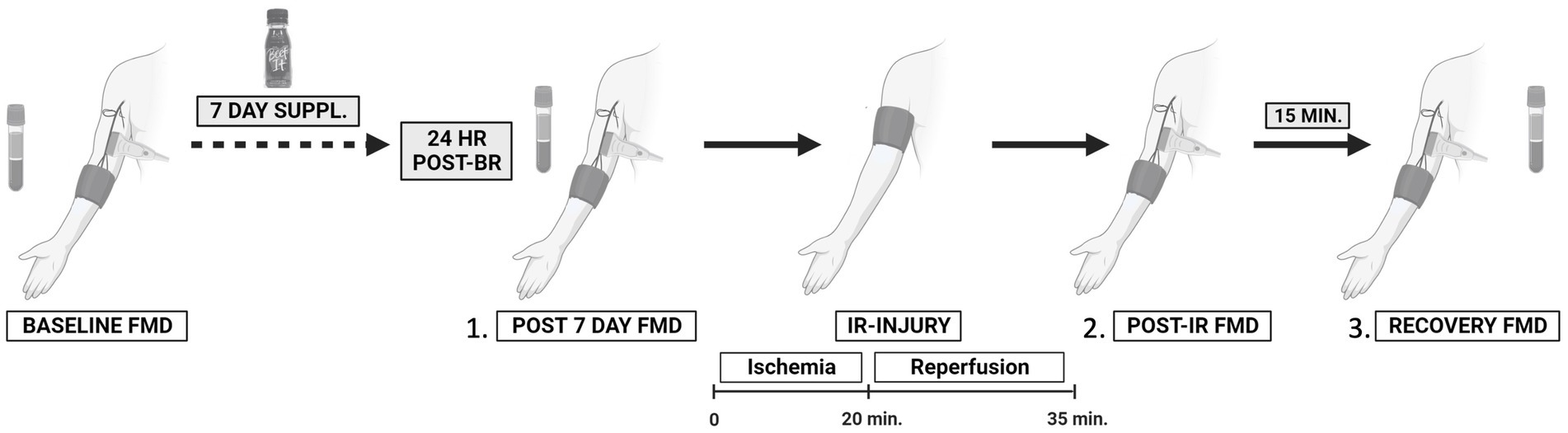
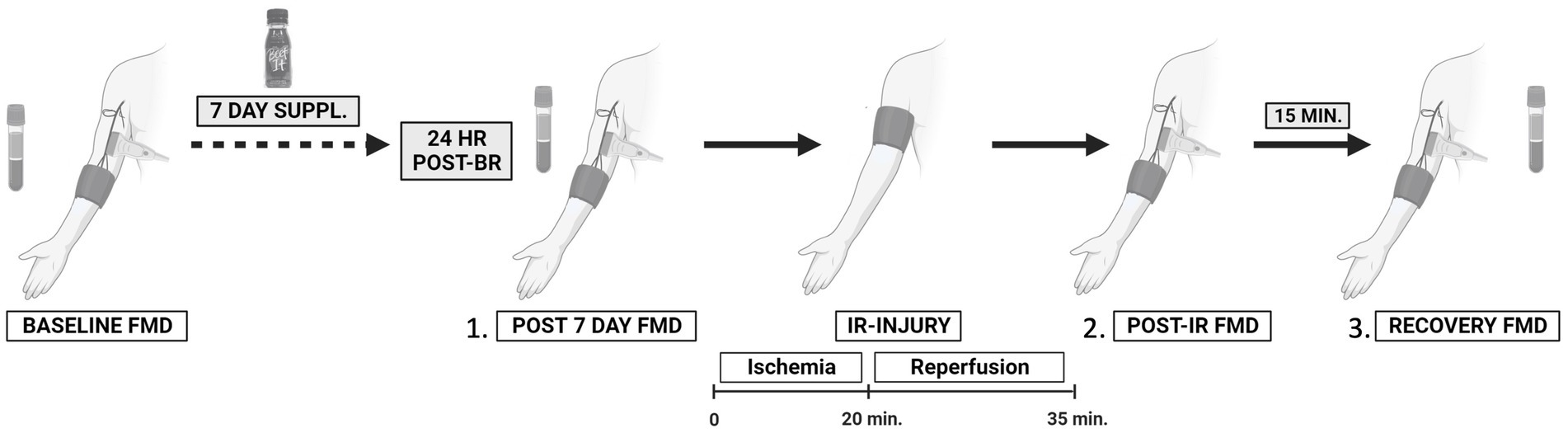
Introduction: Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death in women, with increased risk following menopause. Dietary intake of beetroot juice and other plant-based nitrate-rich foods is a promising non-pharmacological strategy for increasing systemic nitric oxide and improving endothelial function in elderly populations. The purpose of this randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, crossover clinical trial was to determine the effects of short-term dietary nitrate (NO3–) supplementation, in the form of beetroot juice, on resting macrovascular endothelial function and endothelial resistance to whole-arm ischemia–reperfusion (IR) injury in postmenopausal women at two distinct stages of menopause.
Methods: Early-postmenopausal [1–6 years following their final menstrual period (FMP), n = 12] and late-postmenopausal (6+ years FMP, n = 12) women consumed nitrate-rich (400 mg NO3–/70 mL) and nitrate-depleted beetroot juice (approximately 40 mg NO3–/70 mL, placebo) daily for 7 days. Brachial artery flow-mediated dilation (FMD) was measured pre-supplementation (Day 0), and approximately 24 h after the last beetroot juice (BR) dose (Day 8, post-7-day BR). Consequently, FMD was measured immediately post-IR injury and 15 min later (recovery).
Results: Results of the linear mixed-effects model revealed a significantly greater increase in resting FMD with 7 days of BRnitrate compared to BRplacebo (mean difference of 2.21, 95% CI [0.082, 4.34], p = 0.042); however, neither treatment blunted the decline in post-IR injury FMD in either postmenopausal group. Our results suggest that 7-day BRnitrate-mediated endothelial protection is lost within the 24-h period following the final dose of BRnitrate.
Conclusion: Our findings demonstrate that nitrate-mediated postmenopausal endothelial protection is dependent on the timing of supplementation in relation to IR injury and chronobiological variations in dietary nitrate metabolism.
Clinical trial registration: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03644472