2024-06-12 ワシントン大学セントルイス校
<関連情報>
- https://source.wustl.edu/2024/06/artificial-intelligence-tool-may-enhance-usability-of-medical-images/
- https://engineering.wustl.edu/news/2024/DEMIST-artificial-intelligence-tool-may-enhance-usability-of-medical-images.html
- https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10477616
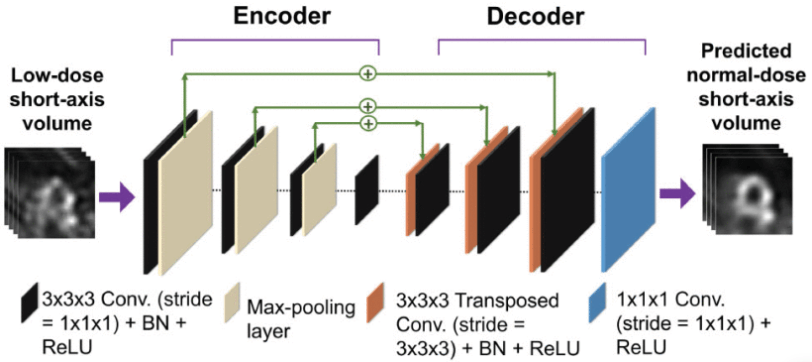
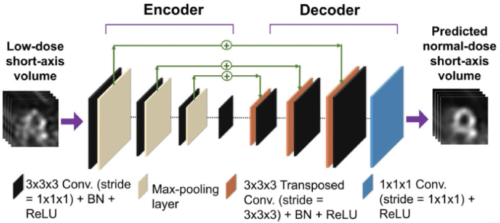
DEMIST:心筋灌流SPECTのためのディープラーニングベースの検出タスク特異的ノイズ除去アプローチ DEMIST: A Deep-Learning-Based Detection-Task-Specific Denoising Approach for Myocardial Perfusion SPECT
Md Ashequr Rahman; Zitong Yu; Richard Laforest; …
IEEE Transactions on Radiation and Plasma Medical Sciences Published:25 March 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1109/TRPMS.2024.3379215
Abstract
There is an important need for methods to process myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI) single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) images acquired at lower-radiation dose and/or acquisition time such that the processed images improve observer performance on the clinical task of detecting perfusion defects compared to low-dose images. To address this need, we build upon concepts from model-observer theory and our understanding of the human visual system to propose a detection task-specific deep-learning-based approach for denoising MPI SPECT images (DEMIST). The approach, while performing denoising, is designed to preserve features that influence observer performance on detection tasks. We objectively evaluated DEMIST on the task of detecting perfusion defects using a retrospective study with anonymized clinical data in patients who underwent MPI studies across two scanners ( N= 338). The evaluation was performed at low-dose levels of 6.25%, 12.5%, and 25% and using an anthropomorphic channelized Hotelling observer. Performance was quantified using area under the receiver operating characteristics curve (AUC). Images denoised with DEMIST yielded significantly higher AUC compared to corresponding low-dose images and images denoised with a commonly used task-agnostic deep learning-based denoising method. Similar results were observed with stratified analysis based on patient sex and defect type. Additionally, DEMIST improved visual fidelity of the low-dose images as quantified using root mean squared error and structural similarity index metric. A mathematical analysis revealed that DEMIST preserved features that assist in detection tasks while improving the noise properties, resulting in improved observer performance. The results provide strong evidence for further clinical evaluation of DEMIST to denoise low-count images in MPI SPECT.