2024-07-22 ペンシルベニア州立大学(PennState)
<関連情報>
- https://www.psu.edu/news/research/story/new-drug-target-identified-diseases-associated-leukemia-causing-virus/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-49737-5
チロシンキナーゼKDRはHTLV-1感染T細胞の生存に必須で、Taxオンコプロテインを安定化させる The tyrosine kinase KDR is essential for the survival of HTLV-1-infected T cells by stabilizing the Tax oncoprotein
Suchitra Mohanty,Sujit Suklabaidya,Alfonso Lavorgna,Takaharu Ueno,Jun-ichi Fujisawa,Nyater Ngouth,Steven Jacobson & Edward W. Harhaj
Nature Communications Published:25 June 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-49737-5
Abstract
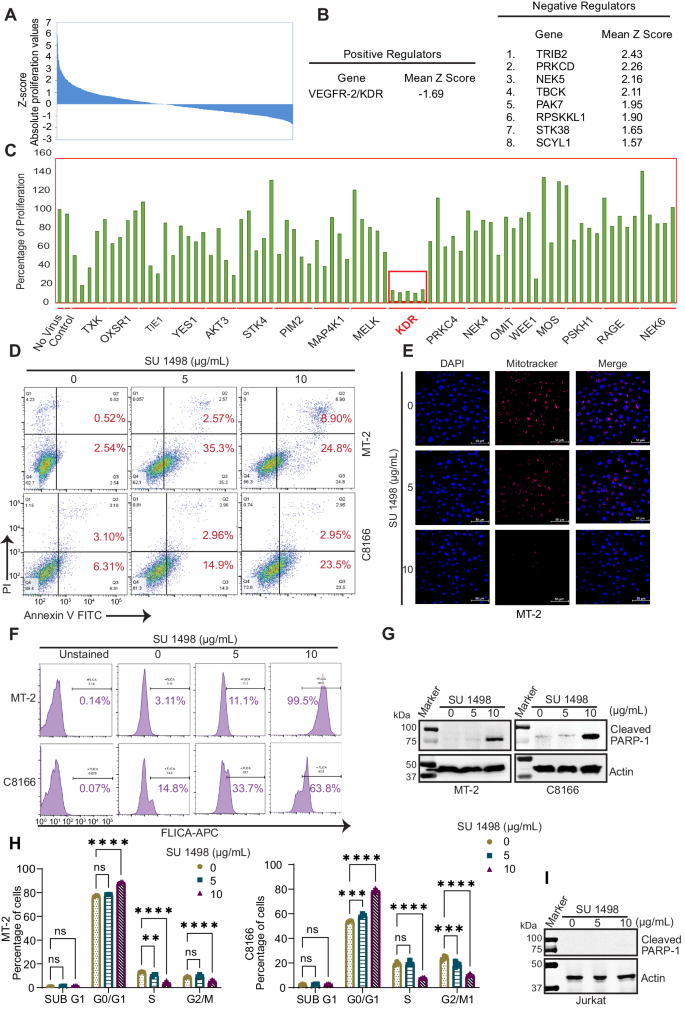
Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) infection is linked to the development of adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATLL) and the neuroinflammatory disease, HTLV-1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis (HAM/TSP). The HTLV-1 Tax oncoprotein regulates viral gene expression and persistently activates NF-κB to maintain the viability of HTLV-1-infected T cells. Here, we utilize a kinome-wide shRNA screen to identify the tyrosine kinase KDR as an essential survival factor of HTLV-1-transformed cells. Inhibition of KDR specifically induces apoptosis of Tax expressing HTLV-1-transformed cell lines and CD4 + T cells from HAM/TSP patients. Furthermore, inhibition of KDR triggers the autophagic degradation of Tax resulting in impaired NF-κB activation and diminished viral transmission in co-culture assays. Tax induces the expression of KDR, forms a complex with KDR, and is phosphorylated by KDR. These findings suggest that Tax stability is dependent on KDR activity which could be exploited as a strategy to target Tax in HTLV-1-associated diseases.


