2024-10-04 カロリンスカ研究所(KI)
<関連情報>
- https://news.ki.se/new-study-brings-hope-to-patients-with-chronic-pain
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-52052-8
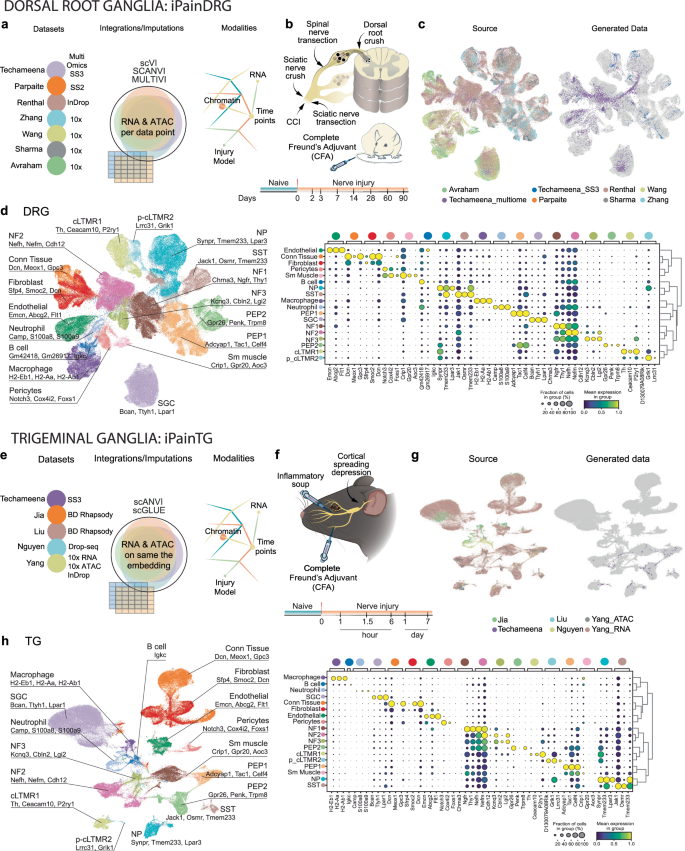
シングルセル・トランスクリプトーム・アトラスiPainが、慢性疼痛治療の標的として侵害受容器の老化を同定 The single-cell transcriptomic atlas iPain identifies senescence of nociceptors as a therapeutical target for chronic pain treatment
Prach Techameena,Xiaona Feng,Kaiwen Zhang & Saida Hadjab
Nature Communications Published:04 October 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-52052-8
Abstract
Chronic pain remains a significant medical challenge with complex underlying mechanisms, and an urgent need for new treatments. Our research built and utilized the iPain single-cell atlas to study chronic pain progression in dorsal root and trigeminal ganglia. We discovered that senescence of a small subset of pain-sensing neurons may be a driver of chronic pain. This mechanism was observed in animal models after nerve injury and in human patients diagnosed with chronic pain or diabetic painful neuropathy. Notably, treatment with senolytics, drugs that remove senescent cells, reversed pain symptoms in mice post-injury. These findings highlight the role of cellular senescence in chronic pain development, demonstrate the therapeutic potential of senolytic treatments, and underscore the value of the iPain atlas for future pain research.