2025-01-13 スウェーデン王立工科大学 (KTH)
<関連情報>
- https://www.kth.se/en/om/nyheter/centrala-nyheter/ai-battre-pa-att-upptacka-aggstockscancer-1.1378780
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-024-03329-4
AIによる卵巣がん超音波検診の国際的多施設共同検証 International multicenter validation of AI-driven ultrasound detection of ovarian cancer
Filip Christiansen,Emir Konuk,Adithya Raju Ganeshan,Robert Welch,Joana Palés Huix,Artur Czekierdowski,Francesco Paolo Giuseppe Leone,Lucia Anna Haak,Robert Fruscio,Adrius Gaurilcikas,Dorella Franchi,Daniela Fischerova,Elisa Mor,Luca Savelli,Maria Àngela Pascual,Marek Jerzy Kudla,Stefano Guerriero,Francesca Buonomo,Karina Liuba,Nina Montik,Juan Luis Alcázar,Ekaterini Domali,Nelinda Catherine P. Pangilinan,Chiara Carella,… Elisabeth Epstein
Nature Medicine Published:02 January 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-024-03329-4
Abstract
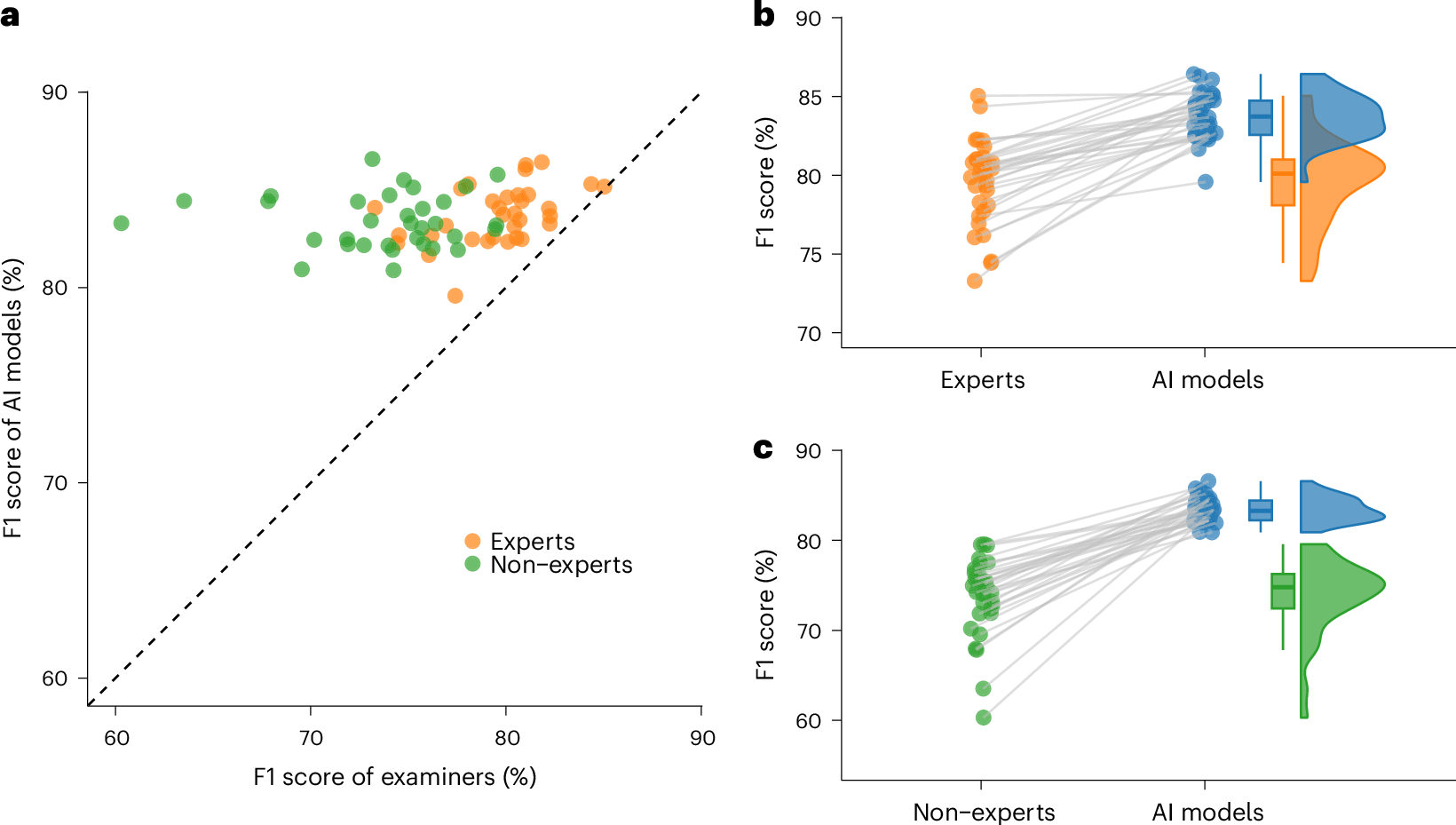
Ovarian lesions are common and often incidentally detected. A critical shortage of expert ultrasound examiners has raised concerns of unnecessary interventions and delayed cancer diagnoses. Deep learning has shown promising results in the detection of ovarian cancer in ultrasound images; however, external validation is lacking. In this international multicenter retrospective study, we developed and validated transformer-based neural network models using a comprehensive dataset of 17,119 ultrasound images from 3,652 patients across 20 centers in eight countries. Using a leave-one-center-out cross-validation scheme, for each center in turn, we trained a model using data from the remaining centers. The models demonstrated robust performance across centers, ultrasound systems, histological diagnoses and patient age groups, significantly outperforming both expert and non-expert examiners on all evaluated metrics, namely F1 score, sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, Cohen’s kappa, Matthew’s correlation coefficient, diagnostic odds ratio and Youden’s J statistic. Furthermore, in a retrospective triage simulation, artificial intelligence (AI)-driven diagnostic support reduced referrals to experts by 63% while significantly surpassing the diagnostic performance of the current practice. These results show that transformer-based models exhibit strong generalization and above human expert-level diagnostic accuracy, with the potential to alleviate the shortage of expert ultrasound examiners and improve patient outcomes.