2025-01-29 ニューサウスウェールズ大学(UNSW)
<関連情報>
- https://www.unsw.edu.au/newsroom/news/2025/01/online-lifestyle-trial-boosts-cognition-in-older-australians-new-study
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-024-03351-6
リスクのある高齢者の認知低下を予防するためのオンライン多領域ライフスタイル介入:無作為化比較試験 An online multidomain lifestyle intervention to prevent cognitive decline in at-risk older adults: a randomized controlled trial
Henry Brodaty,Tiffany Chau,Megan Heffernan,Jeewani A. Ginige,Gavin Andrews,Michael Millard,Perminder S. Sachdev,Kaarin J. Anstey,Nicola T. Lautenschlager,John J. McNeil,Louisa Jorm,Nicole A. Kochan,Anthony Maeder,Heidi Welberry,Juan Carlo San Jose,Nancy E. Briggs,Gordana Popovic,Yorgi Mavros,Carolina Almendrales Rangel,Yian Noble,Sue Radd-Vagenas,Victoria M. Flood,Fiona O’Leary,Amit Lampit,… Michael Valenzuela
Nature Medicine Published:28 January 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-024-03351-6
Abstract
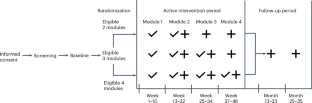
Effective, scalable dementia prevention interventions are needed to address modifiable risk factors given global burden of dementia and challenges in developing disease-modifying treatments. A single-blind randomized controlled trial assessed an online multidomain lifestyle intervention to prevent cognitive decline over 3 years. Participants were dementia-free community-dwelling Australians aged 55–77 years with modifiable dementia risk factors. Eligible participants (n = 6,104, 64% female) were randomized 1:1 to a personalized schedule of online coaching in two to four modules (targeting physical activity, nutrition, cognitive activity and depression or anxiety) or a control group that received module-eligible information only. At 3 years, the mean change in a global cognitive composite, the primary outcome, was met. The mean changes in z scores were 0.28 (95% confidence interval (CI): 0.25–0.32) for intervention, 0.10 (95% CI: 0.07–0.13) for control and 0.18 (95% CI: 0.13–0.23, P < 0.001) for the between-group difference. Trial-related adverse events occurred in 19 (0.60%) intervention and 1 (0.03%) control participant. Randomization of this internet-delivered lifestyle intervention tailored to individual dementia risk factors resulted in significantly better cognition in older adults over 3 years. This intervention is scalable with the potential for population-level rollout that may delay cognitive decline in the general community. Australian New Zealand ClinicalTrials.gov registration: ACTRN12618000851268.