2025-01-16 ワシントン大学セントルイス校
<関連情報>
- https://source.washu.edu/2025/01/drug-in-clinical-trials-for-breast-cancer-could-also-treat-some-blood-cancers/
- https://medicine.washu.edu/news/drug-in-clinical-trials-for-breast-cancer-could-also-treat-some-blood-cancers/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-55643-7
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41408-024-01187-4
RSK1は骨髄増殖性新生物および二次性急性骨髄性白血病において利用可能な依存性である RSK1 is an exploitable dependency in myeloproliferative neoplasms and secondary acute myeloid leukemia
Tim Kong,Angelo B. A. Laranjeira,Christopher T. Letson,LaYow Yu,Shuyang Lin,Jared S. Fowles,Daniel A. C. Fisher,Sherwin Ng,Wei Yang,Fan He,Minyoung Youn,Kailen Mark,Ana San Jose,Jingxian Liu,Alexander B. Kim,Maggie J. Cox,Mary C. Fulbright,Aarthi Jayanthan,Gerrit Los,Stacey L. Rentschler,Li Ding,Kathleen M. Sakamoto,Sandra E. Dunn,Grant A. Challen & Stephen T. Oh
Nature Communications Published:16 January 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-55643-7
Abstract
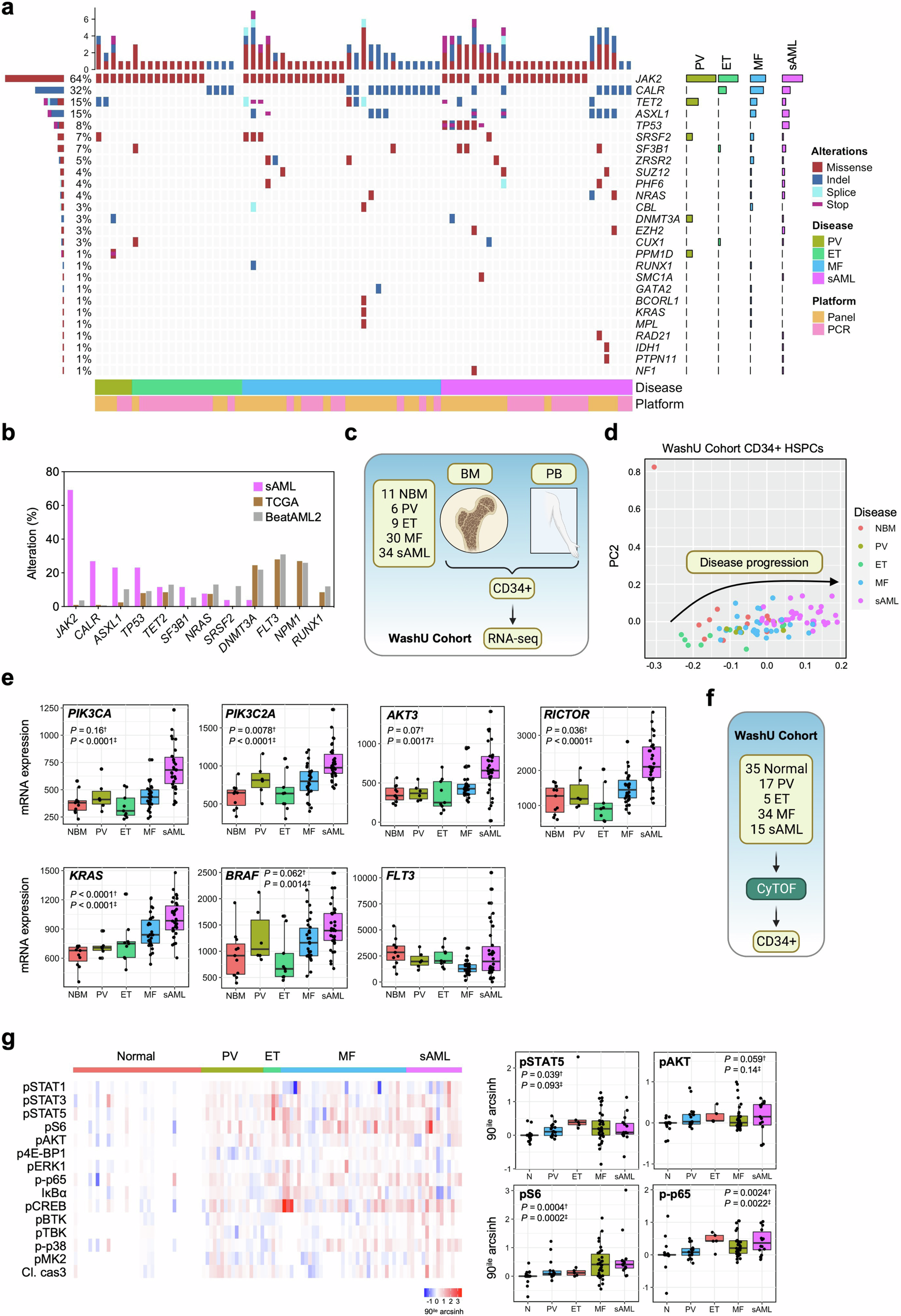
Myeloid malignancies are heterogenous disorders characterized by distinct molecular drivers but share convergence of oncogenic signaling pathways and propagation by ripe pro-inflammatory niches. Here, we establish a comprehensive transcriptional atlas across the spectrum of myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPN) and secondary acute myeloid leukemia (sAML) through RNA-sequencing of 158 primary samples encompassing CD34+ hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells and CD14+ monocytes. Supported by mass cytometry (CyTOF) profiling, we reveal aberrant networks of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling and NFκB-mediated hyper-inflammation. Combining ATAC-Seq, CUT&Tag, RNA-seq, and CyTOF, we demonstrate that targeting of ribosomal protein S6 kinase A1 (RSK1) suppresses NFκB activation and diminishes pro-inflammatory mediators including tumor necrosis factor (TNF) associated with MPN disease severity and transformation. We further evaluate a therapeutic approach utilizing a first-in-class RSK inhibitor, PMD-026, currently in Phase 2 development for breast cancer, for use in myeloid malignancies. Treatment with PMD-026 suppressed disease burden across seven syngeneic and patient-derived xenograft leukemia mouse models spanning the spectrum of driver and disease-modifying mutations. These findings uncover a therapeutic avenue for a conserved dependency across MPN and sAML.
FLT3-ITD急性骨髄性白血病におけるRSK1依存性 RSK1 dependency in FLT3-ITD acute myeloid leukemia
Tim Kong,Angelo B. A. Laranjeira,Christopher T. Letson,LaYow Yu,Fan He,Aarthi Jayanthan,Gerrit Los,Sandra E. Dunn,Grant A. Challen & Stephen T. Oh
Blood Cancer Journal Published:26 November 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41408-024-01187-4

Abstract
Internal tandem duplications (ITD) in fms-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3) represent the most common genetic alteration in de novo acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Here, we identify ribosomal protein s6 kinase a1 (RSK1) as a core dependency in FLT3-ITD AML and unveil the existence of crucial bi-directional regulation. RSK1 perturbation resulted in marked apoptosis and abrogated phosphorylation of FLT3 and associated downstream signaling cascades in FLT3-ITD AML cell lines. Using cycloheximide, MG-132, and ubiquitination assays, we further demonstrate mechanistically that RSK1 regulates FLT3-ITD activity, and protein stability through deubiqutinase USP1, which we identify as a second dependency. Importantly, multivariate analysis revealed heightened expression of RPS6KA1 and USP1 to be associated with poor patient prognosis, and these effectors may serve as biomarkers predictive of patient survival and therapeutic response to FLT3-ITD inhibitors. Lastly, RSK1 inhibition utilizing a first-in-class RSK inhibitor, PMD-026, that is currently undergoing Phase 2 development for breast cancer, diminished leukemic disease burden in MV4-11 xenograft and syngeneic Flt3ITDTet2KO leukemia models. These findings illustrate an unconventional and promising therapeutic strategy targeting FLT3-ITD leukemia.

