2025-03-03 コロンビア大学
<関連情報>
- https://www.cuimc.columbia.edu/news/sleep-patterns-may-reveal-comatose-patients-hidden-consciousness
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-025-03578-x
急性脳損傷後の認知運動解離と意識回復の予測因子としての睡眠紡錘 Sleep spindles as a predictor of cognitive motor dissociation and recovery of consciousness after acute brain injury
Elizabeth E. Carroll,Qi Shen,Vedant Kansara,Nicole Casson,Andrew Michalak,Itamar Niesvizky-Kogan,Jaehyung Lim,Amy Postelnik,Matthew J. Viereck,Satoshi Egawa,Joshua Kahan,Jerina C. Carmona,Lucie Kruger,You Lim Song,Angela Velazquez,Catherine A. Schevon,E. Sander Connolly,Shivani Ghoshal,Sachin Agarwal,David Roh,Soojin Park,Paul Kent & Jan Claassen
Nature Medicine Published:03 March 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-025-03578-x
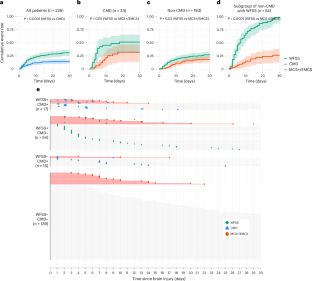
Abstract
Cognitive motor dissociation (CMD) can improve the accuracy to predict recovery of behaviorally unresponsive patients with acute brain injury, but acquisition and analysis of task-based electroencephalography (EEG) are technically challenging. N2 sleep patterns, such as sleep spindles on EEG, have been associated with good outcomes, rely on similar thalamocortical networks as consciousness and could provide less technically challenging complementary outcome predictors. In this prospective observational cohort study of 226 acutely brain injured patients, well-formed sleep spindles (WFSS) were more likely present in those with CMD than in those without CMD, often preceding the detection of CMD. WFSS were associated with a shorter time to recovery of consciousness, and both CMD and WFSS independently predicted recovery of independence, controlling for age, admission neurological status and injury type. WFSS are seen in approximately every third behaviorally unresponsive patient after acute brain injury, frequently precede detection of CMD and are a promising complementary predictor for recovery of consciousness and functional independence.