2025-03-31 カロリンスカ研究所(KI)
<関連情報>
- https://news.ki.se/researchers-have-mapped-the-genetics-of-cardiovascular-disease
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-57457-7#citeas
画像で定義されたアテローム性動脈硬化症のゲノムワイド関連研究 A genome-wide association study of imaging-defined atherosclerosis
Anders Gummesson,Per Lundmark,Qiao Sen Chen,Elias Björnson,Koen F. Dekkers,Ulf Hammar,Martin Adiels,Yunzhang Wang,Therese Andersson,Göran Bergström,Carl-Johan Carlhäll,David Erlinge,Tomas Jernberg,Fredrik Landfors,Lars Lind,Maria Mannila,Olle Melander,Carlo Pirazzi,Johan Sundström,Carl Johan Östgren,Cecilia Gunnarsson,Marju Orho-Melander,Stefan Söderberg,Tove Fall & Bruna Gigante
Nature Communications Published:31 March 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-57457-7
Abstract
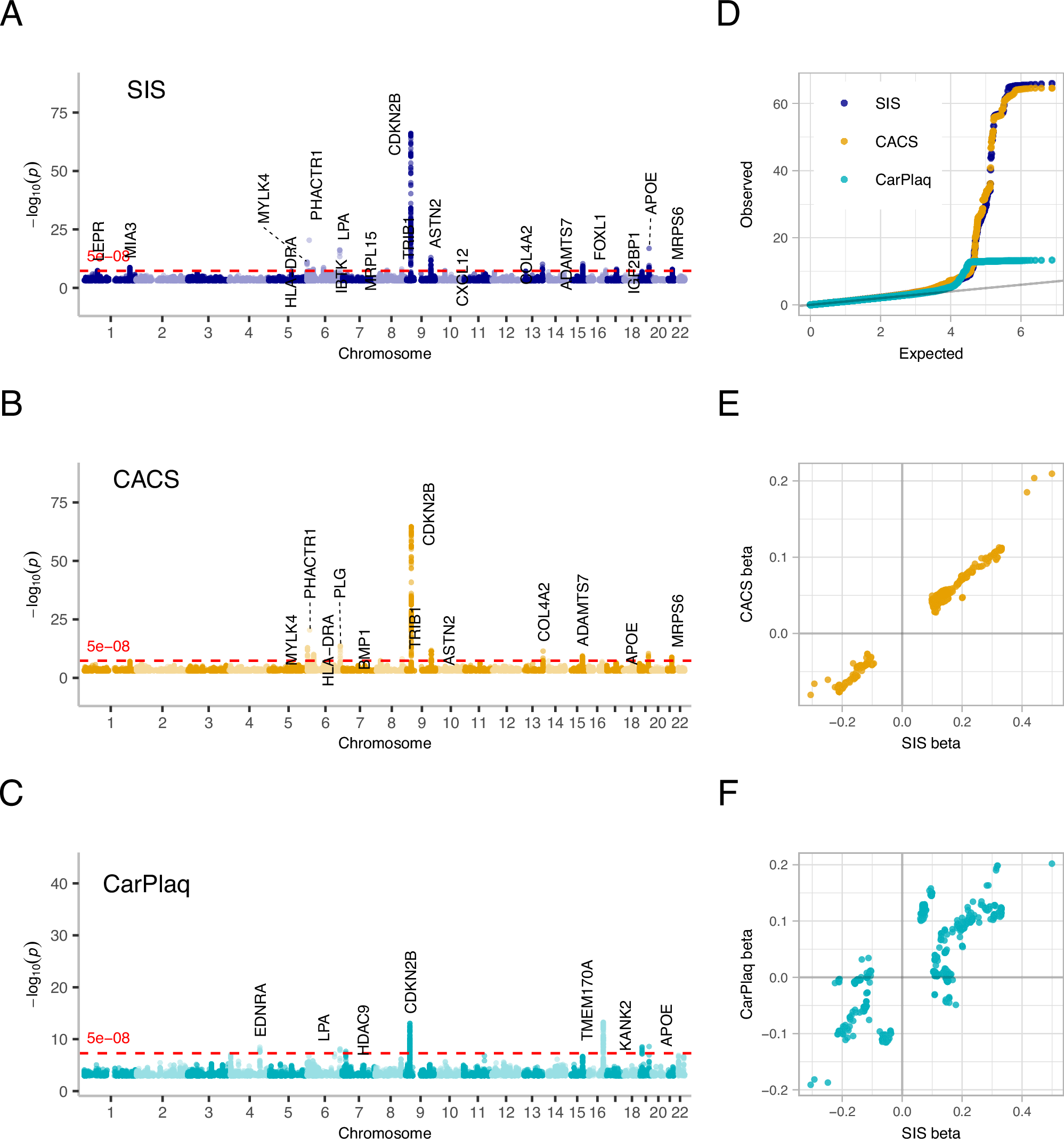
Imaging-defined atherosclerosis represents an intermediate phenotype of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD). Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) on directly measured coronary plaques using coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) are scarce. In the so far largest population-based cohort with CCTA data, we performed a GWAS on coronary plaque burden as determined by the segment involvement score (SIS) in 24,811 European individuals. We identified 20 significant independent genetic markers for SIS, three of which were found in loci not implicated in ASCVD before. Further GWAS on coronary artery calcification showed similar results to that of SIS, whereas a GWAS on ultrasound-assessed carotid plaques identified both shared and non-shared loci with SIS. In two-sample Mendelian randomization studies using SIS-associated markers in UK Biobank and CARDIoGRAMplusC4D, one extra coronary segment with atherosclerosis corresponded to 1.8-fold increased odds of myocardial infarction. This GWAS data can aid future studies of causal pathways in ASCVD.