2025-05-14 東京科学大学
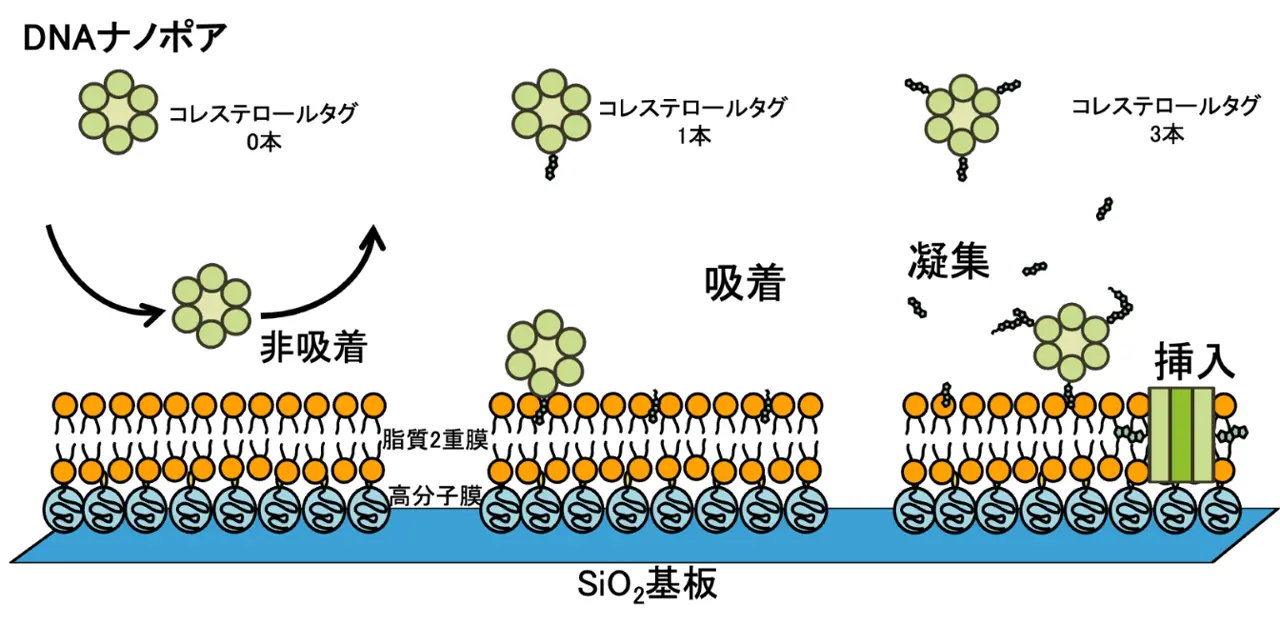
高分子で被覆したシリコン酸化膜(SiO2支持基板)上に作製した脂質二重膜(人工細胞膜)へのDNAナノポアの挿入の模式図。ナノポアに付与したコレステロール基の数によって、吸着・挿入の様式が異なる。
<関連情報>
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/ja/news/2otoq6dor7ny
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/plugins/cms/component_download_file.php?type=2&pageId=&contentsId=1&contentsDataId=1547&prevId=&key=9e78e7b8388d7196fc6c83d1588389c6.pdf
- https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2025/nr/d5nr01299f
QCM-Dを用いたDNAナノ細孔と脂質二重膜の相互作用の時間経過の解明:コレステロールアンカーと二重膜支持基質の役割 Unraveling the time course of interaction between DNA nanopores and lipid bilayers using QCM-D: role of cholesterol anchors and bilayer supporting substrates
Zugui Peng, Glenn Villena Latag, Hiroyuki Tahara, Tohru Yagi and Tomohiro Hayashi
Nanoscale Published:15 Apr 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1039/D5NR01299F
Abstract
Lipid membranes are fundamental elements of cells, serving as barriers that protect the cell interior from the external environment. DNA nanostructures, which can engineer lipid membranes’ signal transduction and substance exchange properties, attract interest for their potential applications in the biomedical field. The interaction between DNA nanostructures and lipid membranes is of scientific and technological interest. Here, we investigate the interaction between DNA nanopores (DNPs) and model supported lipid bilayers (SLBs) using real-time quartz crystal microbalance with energy dissipation monitoring (QCM-D). The long observation time and high temporal resolution enable us to visualize the time course of DNPs’ interaction with SLBs, including their tethering and incorporating processes. Benefiting from the ability of QCM-D to obtain adsorbed layers’ viscoelasticity profiles, we found that the DNPs with three cholesterol tags aggregate and form a rigid layer on the SLB surface during their tethering step. Moreover, our results reveal that the supporting substrates of SLBs impact the incorporation of DNPs, whereby separating the SLBs from the SiO2 sensor surface with poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) polymer cushion results in faster incorporation. This study not only sheds light on the behavior of DNPs but also establishes QCM-D as an analytical platform for exploring the interactions of membrane-interacting DNA nanostructures, potentially accelerating advancements in DNA nanotechnology.