2025-05-16 東京科学大学
 口唇口蓋裂の発症に関わる一塩基多型rs3741442の解析
口唇口蓋裂の発症に関わる一塩基多型rs3741442の解析
<関連情報>
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/ja/news/5b2t0udggt11
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/plugins/cms/component_download_file.php?type=2&pageId=&contentsId=1&contentsDataId=1535&prevId=&key=324868e65cba78e433a846cfa48e10b3.pdf
- https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/00220345251334385
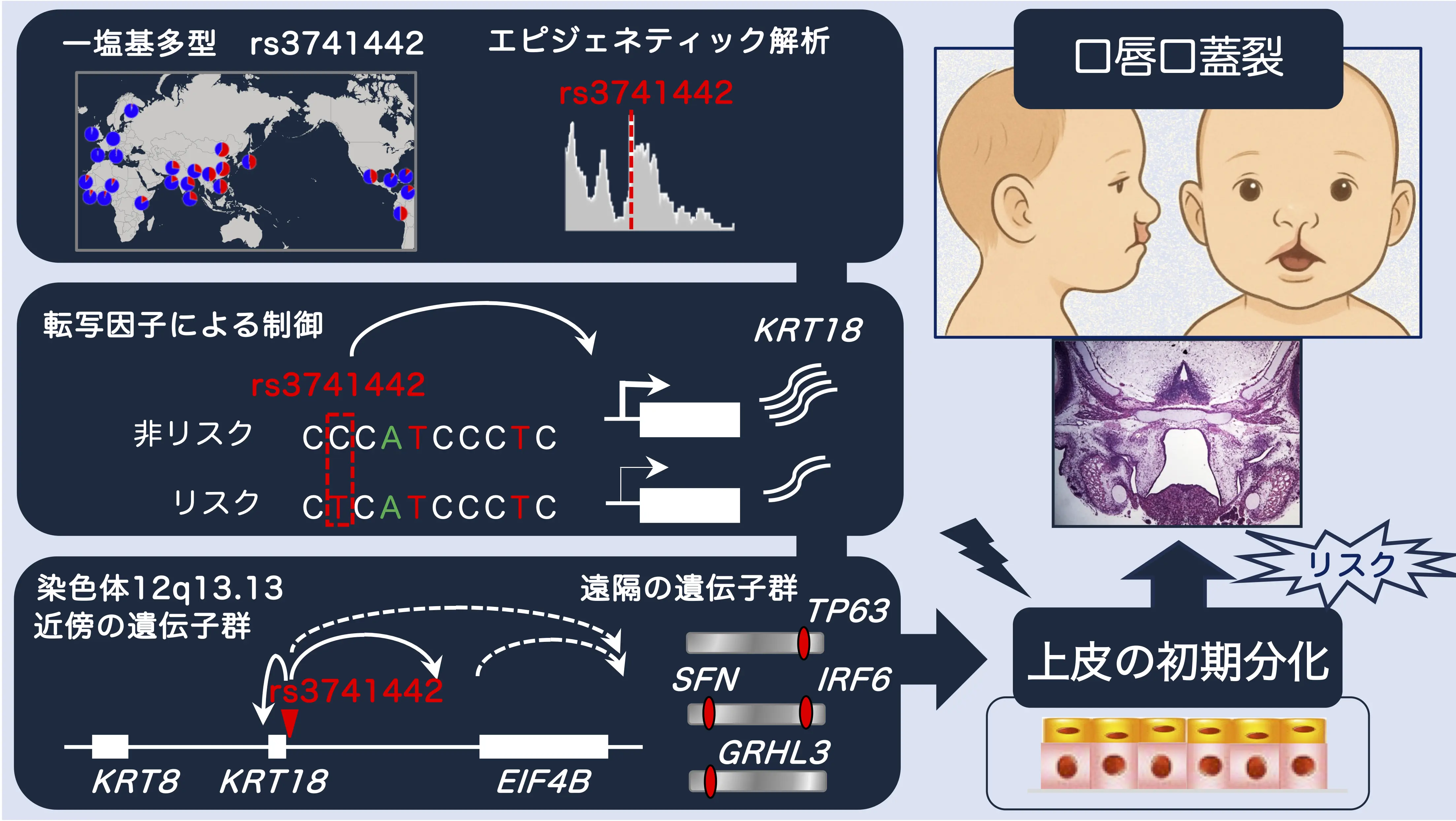
非コードSNP rs3741442の顔面裂隙に対する機能的影響 The Functional Impact of the Noncoding SNP rs3741442 on Orofacial Clefting
N. Funato and S.R.F. Twigg
Journal of Dental Research Published:May 12, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1177/00220345251334385
Abstract
Orofacial cleft (OFC) is a common congenital anomaly in humans with variable birth prevalence in different ethnic groups. Although genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have identified single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) associated with nonsyndromic OFC (nsOFC), understanding of the underlying biological mechanisms of causative SNPs and genes in nsOFC remains limited. Here, we report that the noncoding SNP, rs3741442, has an expression quantitative trait locus (eQTL) effect on epithelial genes associated with periderm differentiation. Using a combination of epigenetic markers and in silico analysis, we prioritized the intergenic SNP rs3741442 as a potential causal factor in nsOFC. The risk allele of rs3741442 is prevalent in East Asian populations, and its presence in CRISPR-edited cells leads to reduced expression of neighboring KRT18 and EIF4B. The transcription factor SP1 differentially binds the risk versus nonrisk alleles of rs3741442. Alongside this cis-eQTL impact, rs3741442 has a trans-eQTL effect on the epithelial gene TP63 that is associated with syndromic forms of OFC and psoriasis. These findings provide insights into the mechanism by which an intergenic SNP can affect palatogenesis through the modulation of gene expression.