2025-05-16 東京科学大学
<関連情報>
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/ja/news/x2zet5l0szw0
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/plugins/cms/component_download_file.php?type=2&pageId=&contentsId=1&contentsDataId=1358&prevId=&key=0781c2e1fed9c4c9f4622e69ff024d35.pdf
- https://www.jci.org/articles/view/186633
遺伝子-環境相互作用はSLC22A12を介して高インスリン血症と血清尿酸値の関連を修飾する Gene-environment interaction modifies the association between hyperinsulinemia and serum urate levels through SLC22A12
Wataru Fujii, Osamu Yamazaki, Daigoro Hirohama, Ken Kaseda, Emiko Kuribayashi-Okuma, Motonori Tsuji, Makoto Hosoyamada, Yuta Kochi, and Shigeru Shibata
The Journal of Clinical Investigation Published: March 18, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI186633
Abstract
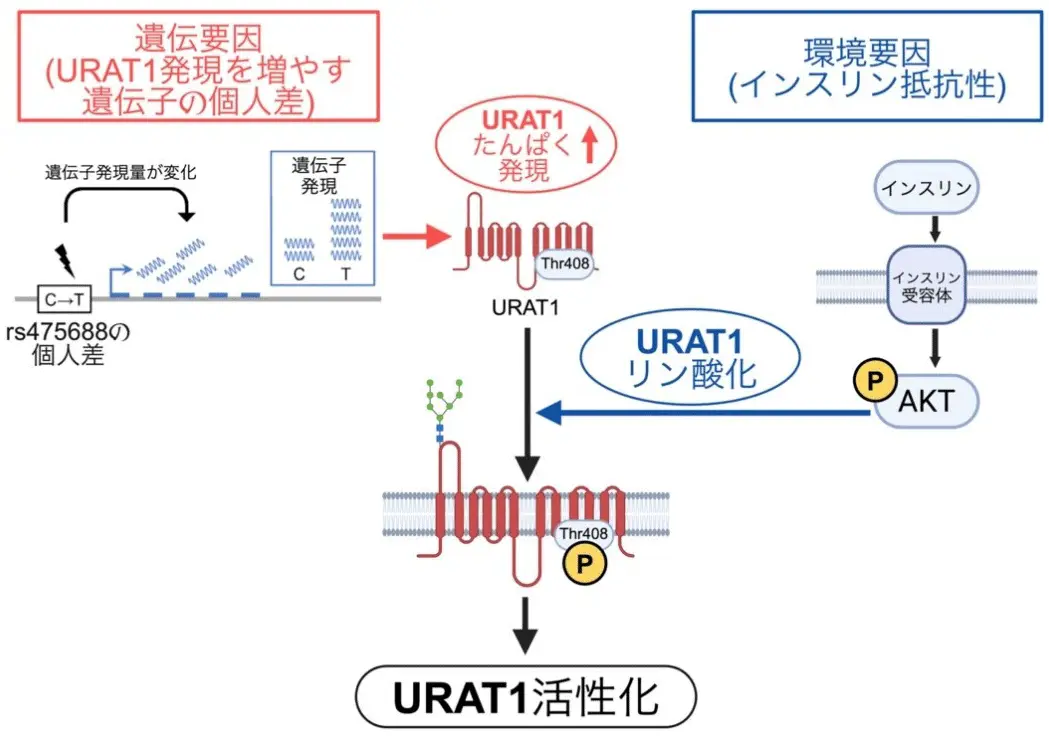
BACKGROUND. Hyperinsulinemia and insulin resistance often accompany elevated serum urate levels (hyperuricemia), a highly heritable condition that triggers gout; however, the underlying mechanisms are unclear.
METHODS. We evaluated the association between the index of hyperinsulinemia and the fractional excretion of urate (FEUA) in 162 outpatients. The underlying mechanisms were investigated through single-cell data analysis and kinase screening combined with cell culture experiments. In 377,358 participants of the UK Biobank (UKBB), we analyzed serum urate, hyperinsulinemia, and salt intake. We also examined gene-environment interactions using single nucleotide variants in SLC22A12, which encodes urate transporter 1 (URAT1).
RESULTS. The index of hyperinsulinemia was inversely associated with FEUA independently of other covariates. Mechanistically, URAT1 cell-surface abundance and urate transport activity were regulated by URAT1-Thr408 phosphorylation, which was stimulated by hyperinsulinemia via AKT. Kinase screening and single-cell data analysis revealed that serum and glucocorticoid-regulated kinase 1 (SGK1), induced by high salt, activated the same pathway, increasing URAT1. Arg405 was essential for these kinases to phosphorylate URAT1-Thr408. In UKBB participants, hyperinsulinemia and high salt intake were independently associated with increased serum urate levels. We found that SLC22A12 expression quantitative trait locus (eQTL) rs475688 synergistically enhanced the positive association between serum urate and hyperinsulinemia.
CONCLUSION. URAT1 mediates the association between hyperinsulinemia and hyperuricemia. Our data provide evidence for the role of gene-environment interactions in determining serum urate levels, paving the way for personalized management of hyperuricemia.
FUNDING. ACRO Research Grants of Teikyo University; Japan Society for the Promotion of Science; the Japanese Society of Gout and Uric & Nucleic Acids; Fuji Yakuhin; Nanken-Kyoten; Medical Research Center Initiative for High Depth Omics.