2025-05-20 韓国基礎科学研究院(IBS)
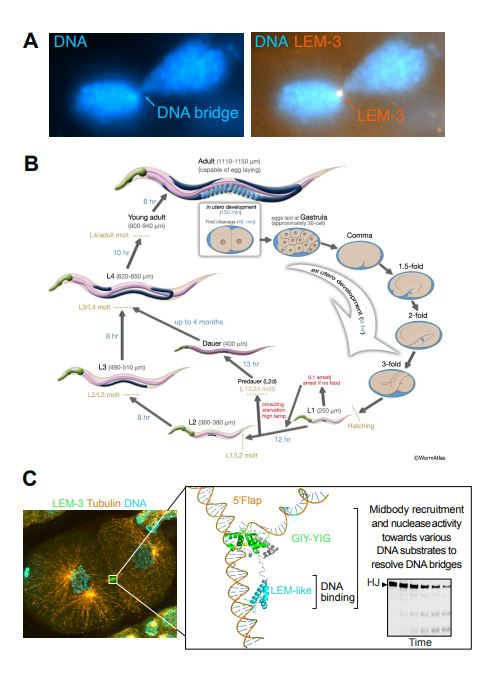
Figure 1. Functional analysis of the LEM-3 protein and the roles of its domains using the C. elegans model.
<関連情報>
- https://www.ibs.re.kr/cop/bbs/BBSMSTR_000000000738/selectBoardArticle.do?nttId=25838
- https://academic.oup.com/nar/article/53/6/gkaf265/8107788
線虫LEM-3/ANKLE1ヌクレアーゼの機能解析から、DNAブリッジ処理にはLEM様ドメインとGIY-YIGドメインが必要であることが明らかになった Functional dissection of the conserved C. elegans LEM-3/ANKLE1 nuclease reveals a crucial requirement for the LEM-like and GIY-YIG domains for DNA bridge processing
Junfang Song , Peter Geary , Khadisha Salemova , John Rouse , Ye Hong , Stéphane G M Rolland , Anton Gartner
Nucleic Acids Research Published:07 April 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaf265
Abstract
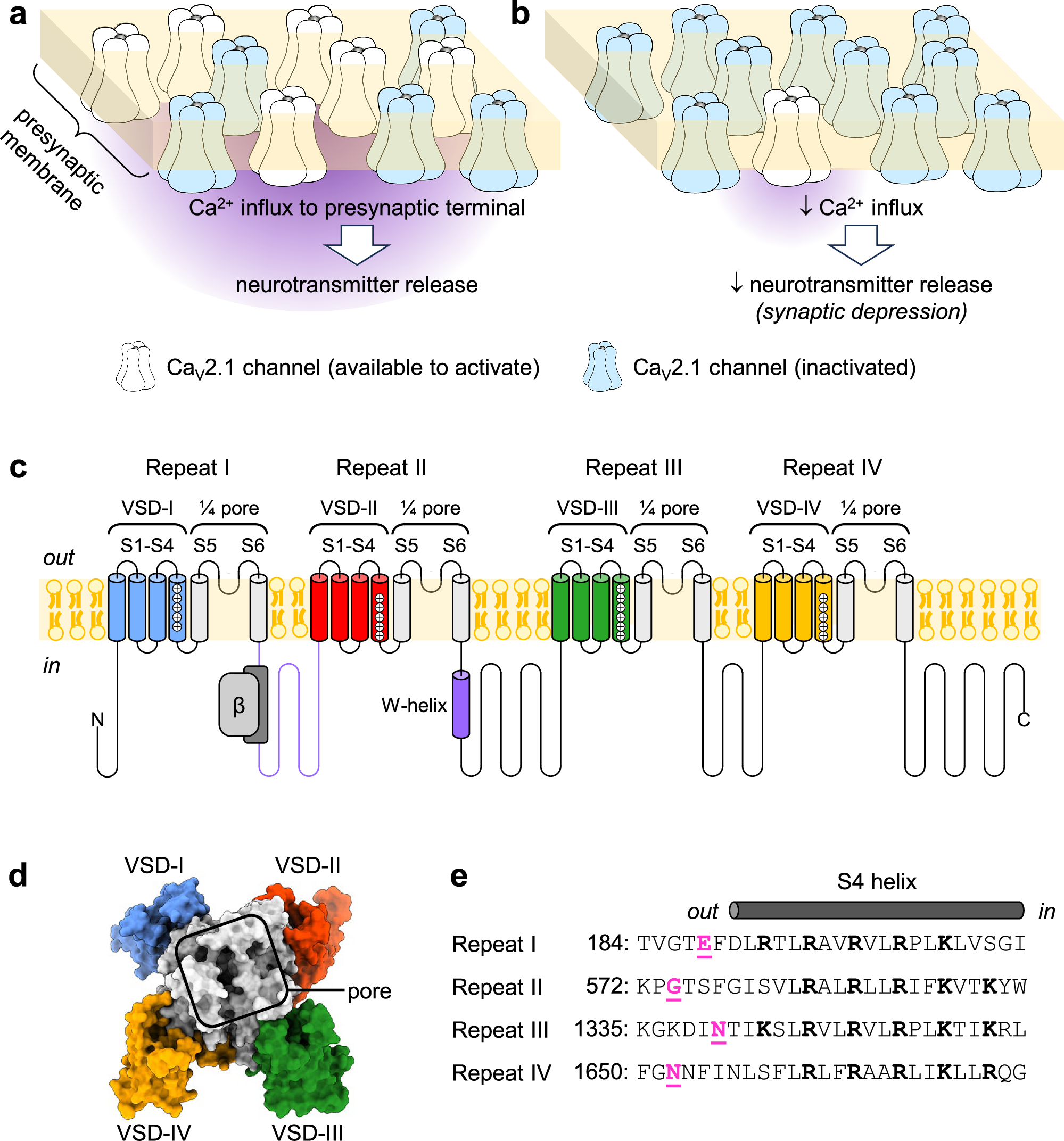
Faithful chromosome segregation requires the removal of all DNA bridges physically linking chromatids before the completion of cell division. While several redundant safeguard mechanisms to process these DNA bridges exist from S-phase to late anaphase, the conserved LEM-3/ANKLE1 nuclease has been proposed to be part of a ‘last chance’ mechanism that acts at the midbody to eliminate DNA bridges that persist until late cytokinesis. We show that LEM-3 can cleave a wide range of branched DNA substrates, including flaps, forks, nicked, and intact Holliday junctions. AlphaFold modelling data suggest that the catalytic mechanism of LEM-3/ANKLE1 is conserved, mirroring the mechanism observed in bacterial GIY-YIG nucleases. We present evidence that LEM-3 may form a homodimeric complex on the Holliday junction DNA. LEM-3 LEM-like and GIY-YIG nuclease domains are essential for LEM-3 recruitment to the midbody and its nuclease activity, while its LEM-like domain is sufficient for DNA binding. Finally, we show that preventing LEM-3 nuclear access is important to avoid toxicity, likely caused by branched DNAs cleavage during normal DNA metabolism. Our data suggest that Caenorhabditis elegans LEM-3 acts as a ‘last chance catch-all’ enzyme that processes DNA bridges caused by various perturbations of DNA metabolism just before cells divide.