2025-05-21 カロリンスカ研究所(KI)
<関連情報>
- https://news.ki.se/a-gene-variant-increases-the-risk-of-long-covid
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41588-025-02100-w
長期COVIDのゲノムワイド関連研究 Genome-wide association study of long COVID
Vilma Lammi,Tomoko Nakanishi,Samuel E. Jones,Shea J. Andrews,Juha Karjalainen,Beatriz Cortés,Heath E. O’Brien,Ana Ochoa-Guzman,Brian E. Fulton-Howard,Martin Broberg,Hele H. Haapaniemi,Masahiro Kanai,Matti Pirinen,Axel Schmidt,Ruth E. Mitchell,Abdou Mousas,Massimo Mangino,Alicia Huerta-Chagoya,Nasa Sinnott-Armstrong,Elizabeth T. Cirulli,Marc Vaudel,Alex S. F. Kwong,Amit K. Maiti,Minttu M. Marttila,Long COVID Host Genetics Initiative,FinnGen,VA Million Veteran Program,MexGen-COVID Initiative,DBDS Genomic Consortium,GEN-COVID Multicenter Study,PHOSP-COVID Collaborative Group,GENCOV Study,Estonian Biobank Research Team,… Hanna M. Ollila
Nature Genetics Published:21 May 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-025-02100-w
Abstract
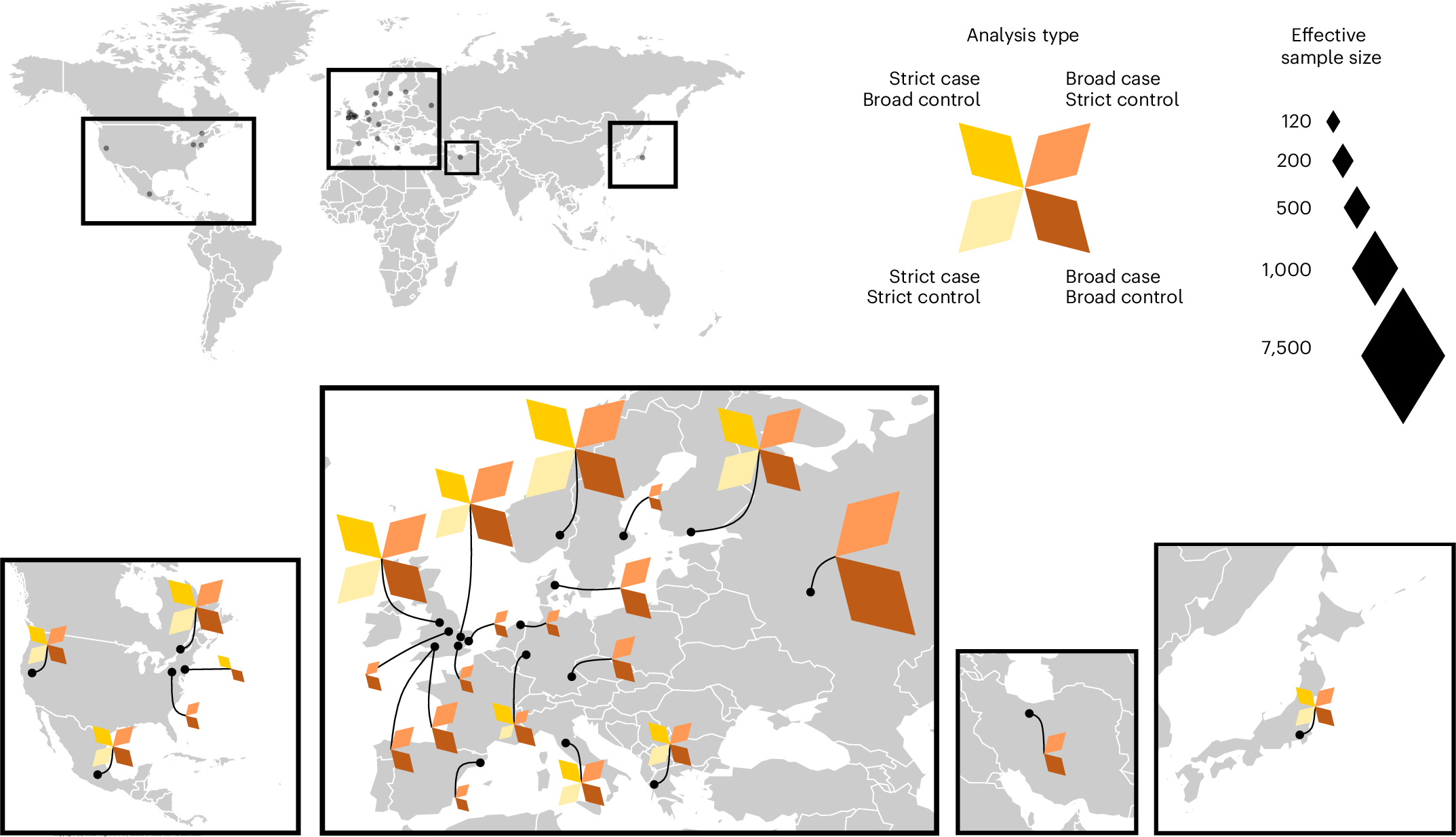
Infections can lead to persistent symptoms and diseases such as shingles after varicella zoster or rheumatic fever after streptococcal infections. Similarly, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2) infection can result in long coronavirus disease (COVID), typically manifesting as fatigue, pulmonary symptoms and cognitive dysfunction. The biological mechanisms behind long COVID remain unclear. We performed a genome-wide association study for long COVID including up to 6,450 long COVID cases and 1,093,995 population controls from 24 studies across 16 countries. We discovered an association of FOXP4 with long COVID, independent of its previously identified association with severe COVID-19. The signal was replicated in 9,500 long COVID cases and 798,835 population controls. Given the transcription factor FOXP4’s role in lung physiology and pathology, our findings highlight the importance of lung function in the pathophysiology of long COVID.