2025-05-26 中国科学院(CAS)
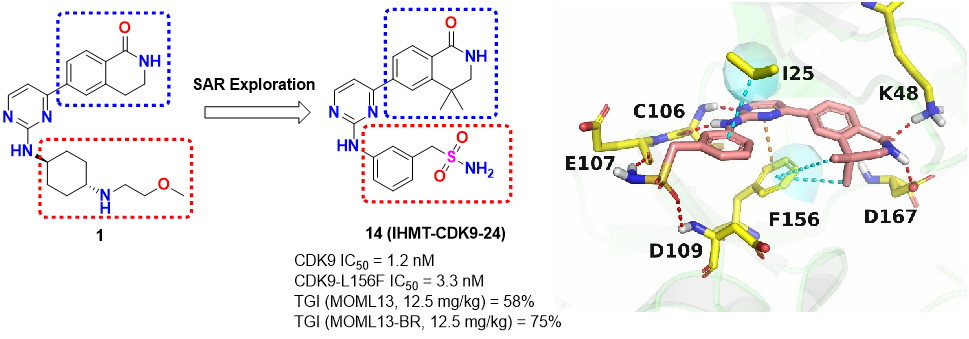
Novel compound IHMT-CDK9-24: Discovery and its potent antitumor activity in vitro and in vivo. (Image by SHI Chenliang)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research-news/202505/t20250527_1131441.shtml
- https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.4c02548
L156F変異体を克服する強力なCDK9阻害剤としての新規ジヒドロイソキノリノン誘導体の発見による血液悪性腫瘍の治療への応用 Discovery of a Novel Dihydroisoquinolinone Derivative as a Potent CDK9 Inhibitor Capable of Overcoming L156F Mutant for the Treatment of Hematologic Malignancies
Chenliang Shi,Yun Wu,Fengming Zou,Yuan Yuan,Chen Hu,Qingwang Liu,Chao Wu,Lijuan Shen,Aoli Wang,Wenchao Wang,Beilei Wang,Jing Liu,and Qingsong Liu
Journal of Medicinal Chemistry Published: April 8, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.4c02548
Abstract
Hematologic malignancies represent the most prevalent type of malignant cancers associated with significant morbidity and mortality rates. Given CDK9’s extensive crosstalk with various signaling pathways and its crucial role in maintaining stem cell phenotypes, it emerges as a promising therapeutic target for hematologic malignancies. Despite ongoing efforts, resistance remains a ubiquitous challenge and significant limitation in the management of these malignancies. Here, we discovered a novel potent and selective inhibitor (14) of both CDK9 wild-type and L156F mutant, which inhibited p-Ser2 RNA Pol II, cMYC, and MCL-1, ultimately triggering apoptosis of hematological cancer cells. In vitro studies further revealed that 14 could efficiently suppress the proliferation of a diverse range of hematological cancer cell lines. Additionally, the in vivo efficacies have been demonstrated in different genetic background hematologic cancer cell-derived mice models. Together, these findings highlight the promising potential of this novel CDK9 inhibitor in the treatment of hematological malignancies.