2025-06-30 中国科学院(CAS)
 LRRC8/VRAC-mediated cGAMP transfer underlines radiotherapy and chemotherapy. (Image by SIII)
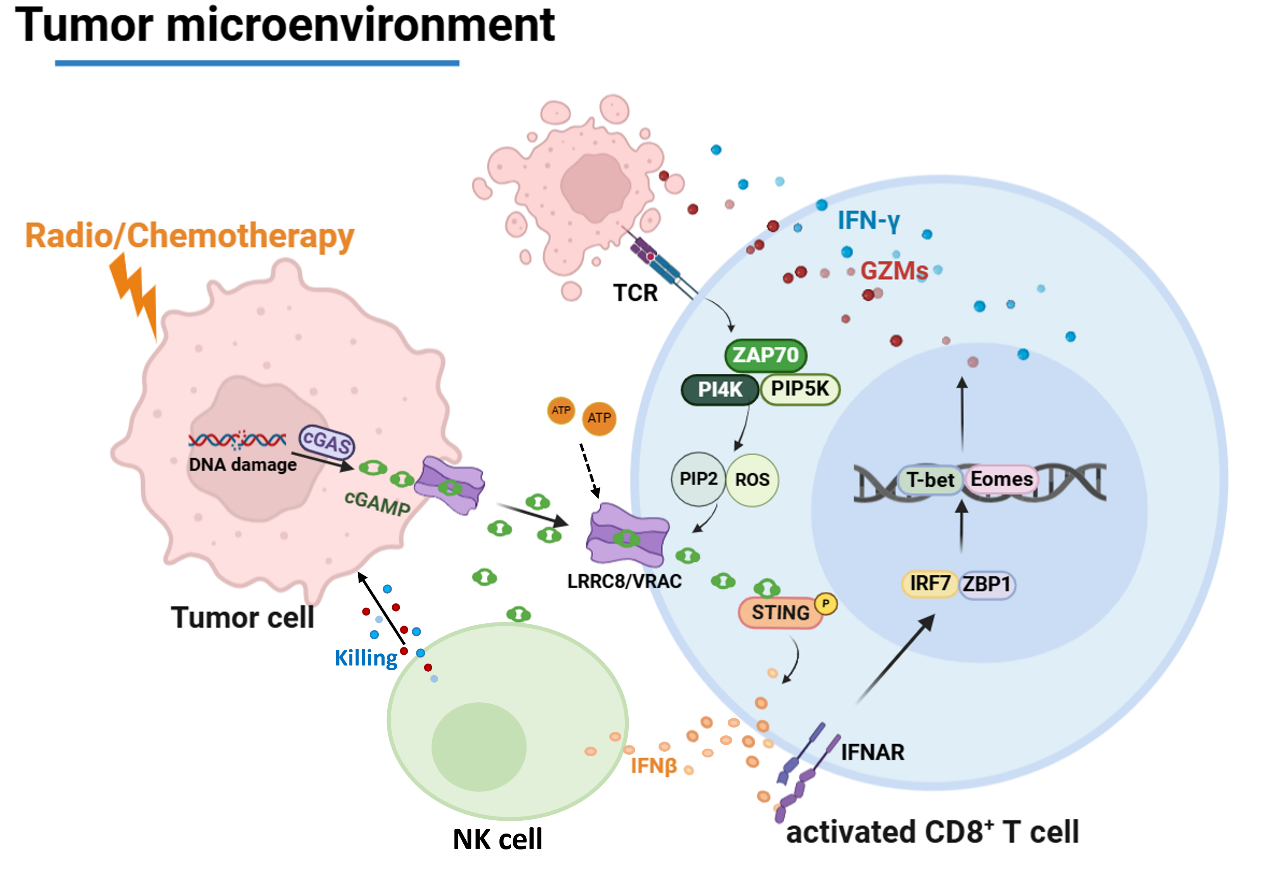
LRRC8/VRAC-mediated cGAMP transfer underlines radiotherapy and chemotherapy. (Image by SIII)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research_news/life/202506/t20250625_1046221.shtml
- https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciimmunol.adn1630
放射線治療はLRRC8A/C体積制御アニオンチャネルを介したcGAMP移動により抗がんCD8 T細胞応答を増強する Radiotherapy enhances anticancer CD8 T cell responses by cGAMP transfer through LRRC8A/C volume-regulated anion channels
Limin Cao, Li Wang, Zhihong Li, Xia Wei, […] , and Hui Xiao
Science Immunology Published:27 Jun 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1126/sciimmunol.adn1630
Editor’s summary
Volume-regulated anion channels (VRACs) transport a wide range of solutes across the cell membrane and are critical to regulating cell volume. Cao et al. now show that the leucine-rich repeat–containing 8A/C (LRRC8A/C) VRAC can transport cyclic GMP-AMP (cGAMP) from irradiated cancer cells into T cells within tumors to enhance their antitumor effector responses. TCR signaling leads to the opening of VRAC pores and transport of cGAMP, which causes STING activation and the subsequent induction of type I IFN and CD8 T cell effector molecules. These results highlight how targeting cGAMP transfer into T cells may be a potential strategy for enhancing antitumor responses. —Christiana N. Fogg
Abstract
The volume-regulated anion channels (VRACs) transport osmolytes, neurotransmitters, and cyclic GMP-AMP (cGAMP) across the cell membrane to regulate cell volume and host defense. We report that the leucine-rich repeat–containing 8A/C (LRRC8A/C) VRAC plays a crucial role in immune responses to radiotherapy and chemotherapy for cancer. VRACs transfer cGAMP from irradiated cancer cells to infiltrating CD4 and CD8 T cells, thus enhancing their effector functions. TCR signaling acts as a physiological signal to open the VRAC pore through phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate [PI(4,5)P2] and reactive oxygen species (ROS). This allows the rapid uptake of cGAMP and STING activation in mouse and human T cells and induction of interferon-α/β, which up-regulate granzymes and IFN-γ in CD8 T cells. Inhibition of the extracellular hydroxylases CD39 and ENPP1 maintains extracellular ATP and cGAMP, which promotes VRAC-enhanced CD8 T cell anticancer function. Thus, the transfer of cGAMP to T cells by VRACs may be a strategy that can be targeted in future cancer therapies.


00194-4/asset/cc4f3fac-0b5f-4e1f-a079-6938e56789ee/main.assets/gr1.jpg)