2025-07-16 中国科学院(CAS)
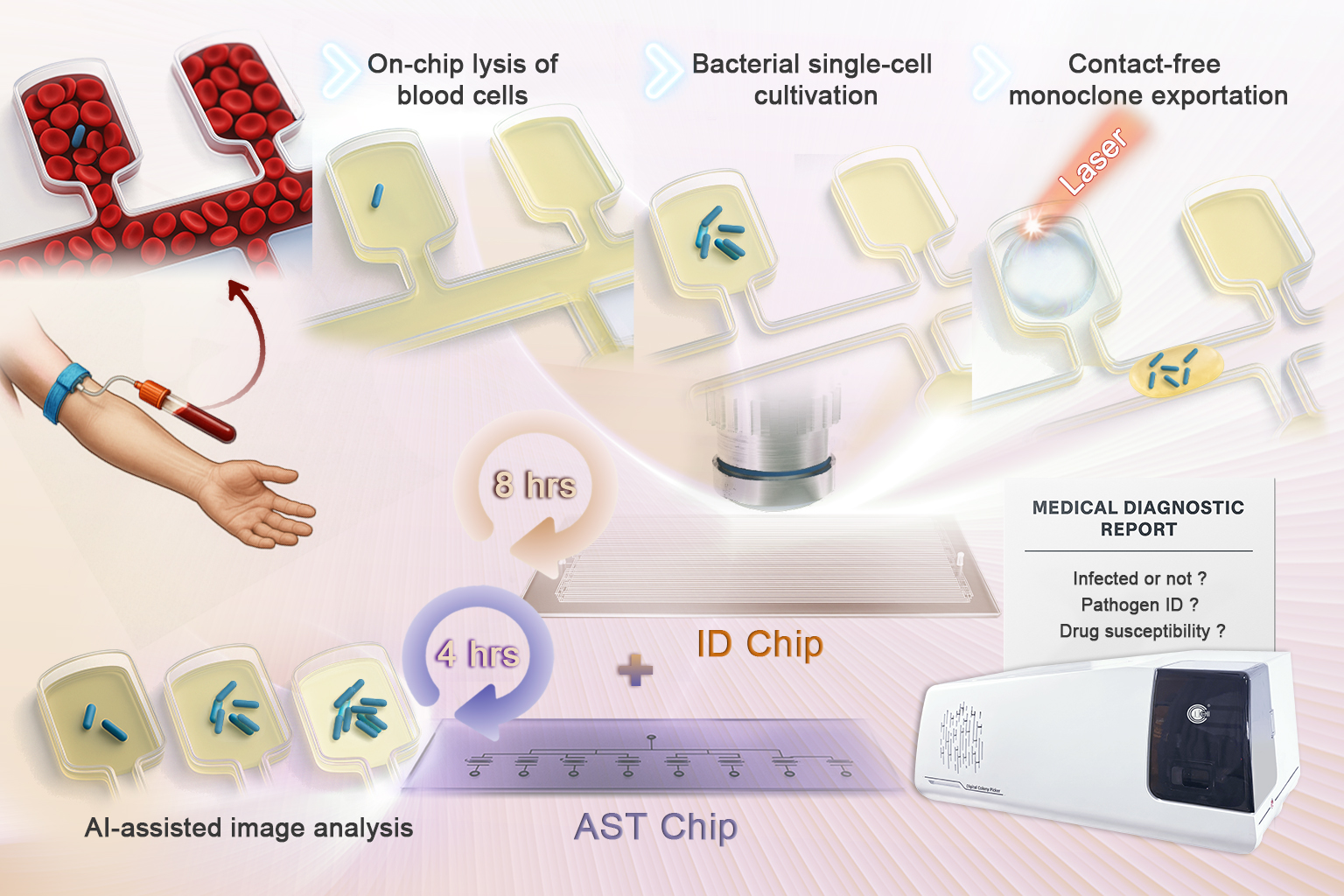
A microfluidic chip-based platform enables rapid detection of pathogens. (Image by QIBEBT)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research_news/life/202507/t20250716_1047468.shtml
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0925400525009591
スタティック・ドロップレット・アレイ(SDA)チップを用いた血液中の病原体の迅速な定量的検出、同定および抗菌薬感受性試験 Rapid quantitative detection, identification and antimicrobial susceptibility testing of pathogens in blood using the static droplet array (SDA) chip-based method
Zhidian Diao, Anle Ge , Hao Zhou, Xuan Zhou, Lingyan Kan, Wei Gao, Wei Shen, Yuetong Ji, Hongwei Wang, Jian Xu, Xixian Wang, Bo Ma
Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical Available online: 24 June 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2025.138183
Highlights
- Static droplet array chip enables rapid quantitative pathogen detection in unprocessed blood and chip-based AST.
- Microchamber array isolates single bacteria for absolute quantification in 3–5 h over 10–10,000 CFU/mL post-lysis.
- AI-assisted image recognition tracks bacterial growth under antibiotics to yield rapid, accurate MIC values.
Abstract
Bloodstream infection (BSI) has emerged as a significant and life-threatening global health concern. Rapid and accurate identification of pathogens in the bloodstream and antimicrobial susceptibility testing (AST) are essential for intervention and treatment. Here, we developed a static droplet array (SDA) chip for the rapid quantitative detection and identification of pathogens in unprocessed blood and subsequent Chip-AST experiments on pathogens. The microchamber array enables isolated individual bacteria in chambers, thus allowing for quantification of bacteria within 3–5 h after cell lysis and medium exchange. The detection limit of the SDA chip can reach 10 CFU/mL. Further export of cultured pathogens from chips allows subsequent strain identification. In addition, artificial intelligence (AI) image recognition is employed in the rapid assessment of AST on pathogen. The entire detection time has been reduced to approximately 12 h, representing a improvement over traditional method. Finally, the experimental process was validated using clinical samples. This microfluidic chip-based detection method offers a promising, rapid, and cost-effective solution for diagnosing BSI and rapid AST, with the potential to improve public health outcomes.

