2025-07-31 東京科学大学
<関連情報>
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/ja/news/vr3wpuoo0tje
- https://publications.ersnet.org/content/erj/early/2025/07/03/1399300301150-2024
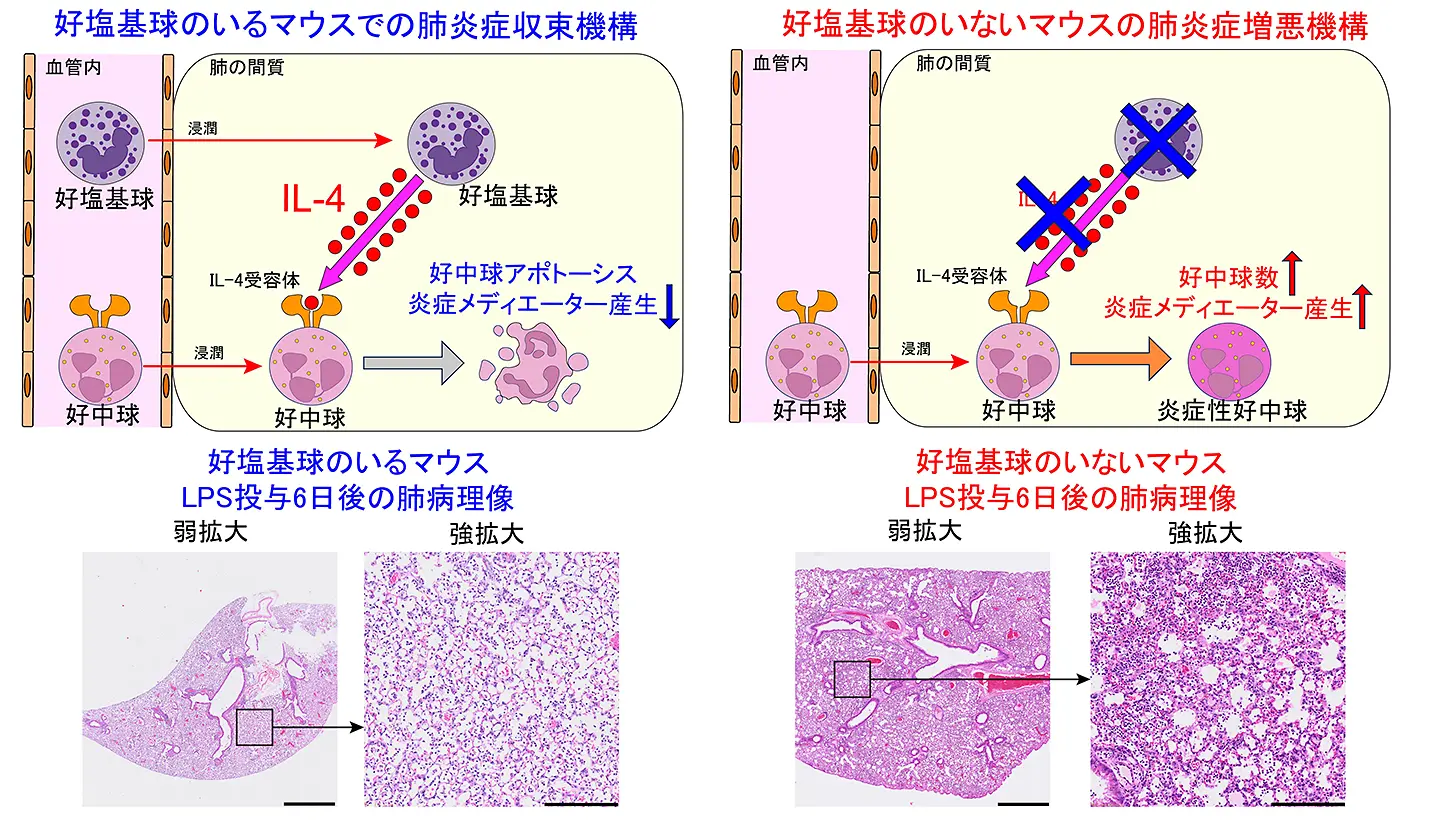
急性呼吸窮迫症候群の解消における好塩基球の新たな役割 Emerging roles of basophils in the resolution of the acute respiratory distress syndrome
Seiko Takasawa,Tomoya Tateishi,Jun Sugihara,…
European Respiratory Journal Published:31 July 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1183/13993003.01150-2024
Abstract
Background
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a severe form of lung failure with a high mortality rate and no effective pharmacological therapy. Although the cellular and molecular mechanisms involved in ARDS onset have been extensively studied, those governing its resolution remain unclear. Recent human cohort studies have suggested an association between ARDS severity and low blood basophil count. Therefore, in this study, we investigated the roles of basophils in ARDS pathogenesis and resolution.
Methods
We examined the effects of basophil depletion in lipopolysaccharide-induced ARDS model mice and assessed the roles of basophils in ARDS onset and resolution using genetically engineered mice and single-cell RNA-sequencing analysis.
Results
Intratracheal administration of lipopolysaccharides induced severe lung inflammation, characterised by extensive neutrophil infiltration, followed by gradual recovery to homeostatic conditions. Basophil depletion impaired the resolution but not the induction of lung inflammation, highlighting the critical role of basophils in the resolution phase of ARDS. Basophils accumulated in the lungs were the primary sources of the cytokine IL-4. Mice with basophil-specific IL-4 deficiency failed to resolve lung inflammation, as did mice with neutrophil-specific IL-4 receptor deficiency. Transcriptomic analysis revealed that basophil-derived IL-4 acted on neutrophils to suppress the anti-apoptotic gene and pro-inflammatory mediator expression.
Conclusions
Overall, our findings revealed that basophils played essential roles in the ARDS resolution phase, primarily by producing IL-4, which acted on neutrophils to alleviate lung inflammation in ARDS model mice.

