2023-04-20 ジョージア工科大学
このモデルは、国全体および各州に対して機能し、公衆衛生当局や病院が直近の大流行を予測するためのデータを提供するものです。研究者たちは、23のキー検索クエリを使用して、重篤なインフルエンザ様疾患とCOVID-19の症例を4週間先まで予測しています。
この研究成果は、Nature誌Communications Medicineに掲載されています。
<関連情報>
- https://coe.gatech.edu/news/2023/04/internet-search-data-can-help-predict-looming-twindemic
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s43856-023-00272-2
インターネット検索情報を利用した米国におけるCOVID-19とインフルエンザ様疾患の共同予測について Joint COVID-19 and influenza-like illness forecasts in the United States using internet search information
Simin Ma,Shaoyang Ning & Shihao Yang
Communications Medicine Published:24 March 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s43856-023-00272-2
Abstract
Background
As the prolonged COVID-19 pandemic continues, severe seasonal Influenza (flu) may happen alongside COVID-19. This could cause a “twindemic”, in which there are additional burdens on health care resources and public safety compared to those occurring in the presence of a single infection. Amidst the raising trend of co-infections of the two diseases, forecasting both Influenza-like Illness (ILI) outbreaks and COVID-19 waves in a reliable and timely manner becomes more urgent than ever. Accurate and real-time joint prediction of the twindemic aids public health organizations and policymakers in adequate preparation and decision making. However, in the current pandemic, existing ILI and COVID-19 forecasting models face shortcomings under complex inter-disease dynamics, particularly due to the similarities in symptoms and healthcare-seeking patterns of the two diseases.
Methods
Inspired by the interconnection between ILI and COVID-19 activities, we combine related internet search and bi-disease time series information for the U.S. national level and state level forecasts. Our proposed ARGOX-Joint-Ensemble adopts a new ensemble framework that integrates ILI and COVID-19 disease forecasting models to pool the information between the two diseases and provide joint multi-resolution and multi-target predictions. Through a winner-takes-all ensemble fashion, our framework is able to adaptively select the most predictive COVID-19 or ILI signals.
Results
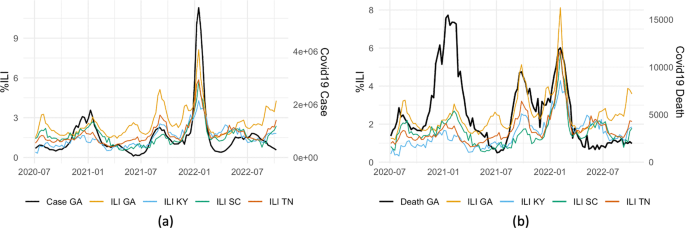
In the retrospective evaluation, our model steadily outperforms alternative benchmark methods, and remains competitive with other publicly available models in both point estimates and probabilistic predictions (including intervals).
Conclusions
The success of our approach illustrates that pooling information between the ILI and COVID-19 leads to improved forecasting models than individual models for either of the disease.
Plain language summary
Data from the internet enables the presence of infectious diseases such as influenza (flu) to be tracked and monitored. During the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic people will also be infected with flu, impacting health care providers. Predicting both COVID-19 and flu outbreaks in a timely manner enables health care providers and policymakers to prepare for the outbreaks. In this work, we develop a model to jointly predict cases of both COVID-19 and influenza-like illness that can be used at national and state levels in the USA. Our approach is more accurate than alternative similar approaches that predict cases of a single disease, showing the value of predicting the incidence of multiple diseases at the same time.