2025-08-06 北海道大学,大阪大学,九州大学
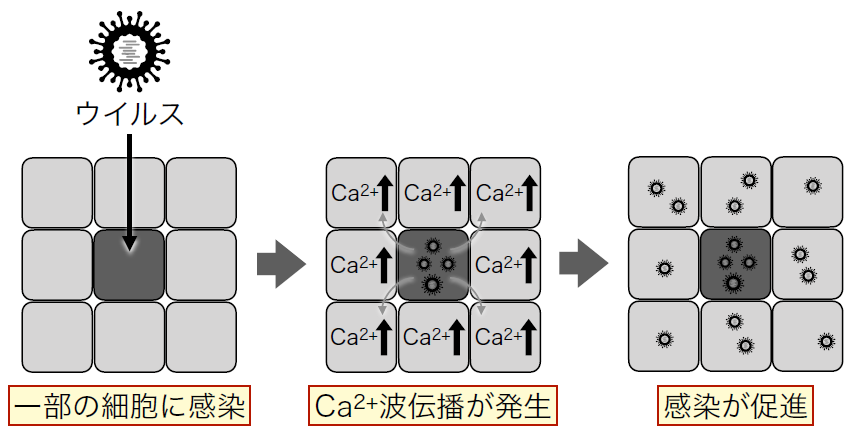
最初に感染した細胞を起点に周囲の細胞にメッセージ(ADP)が送られ、細胞内カルシウムイオン(Ca2+)濃度が上昇する。それに伴い、周囲の細胞で感染が活発に起こる。
<関連情報>
- https://www.hokudai.ac.jp/news/2025/08/post-2009.html
- https://www.hokudai.ac.jp/news/pdf/250806_pr2.pdf
- https://biosignaling.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12964-025-02357-y
細胞間カルシウム波伝播によりインフルエンザウイルス感染が促進される The crucial role of intercellular calcium wave propagation triggered by influenza A virus in promoting infection
Fumiya Kozawa,Tomokazu Tamura,Naoki Takahashi,Taishi Kakizuka,Taro Ichimura,Rumi Shimada,Yasuyuki Hashimoto,Hironoshin Onizuska,Sayaka Kashiwagi,Tomoko Kamasaki,Maho Amano,Takeharu Nagai,Takasuke Fukuhara,Yoichiro Fujioka & Yusuke Ohba
Cell Communication and Signaling Published:02 August 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1186/s12964-025-02357-y
Abstract
Background
Influenza A viruses (IAVs) initially infect a few host cells before spreading to neighboring cells. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying this dissemination remain unclear. We have previously demonstrated that intracellular Ca2+ plays a crucial role in facilitating IAV infection. This study aims to clarify the connections between intracellular Ca2+ dynamics and spread of IAV infection.
Methods
Madin–Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cells stably expressing a Ca2+ indicator for optical imaging were established. Cells were cultured in Matrigel to form monolayers, and cell-to-cell Ca2+ dynamics within IAV-infected cells were analyzed using fluorescence microscopy.
Results
IAV infection upregulated the frequency of intercellular calcium wave propagations (iCWPs), facilitating viral spread. ADP released from initially infected cells mediated iCWPs via the P2Y1 receptor. P2Y1 antagonist suppressed both the generation of iCWPs and spread of viral infection. Enhanced endocytosis by the surrounding cells that received ADP signaling upregulated viral entry. Expression of IAV matrix protein 2 (M2) in initially infected cells triggered iCWPs through ADP diffusion, thereby increasing infection. Conversely, an ion permeability-deficient mutation of M2 or inhibition of its ion channel activity suppressed iCWPs.
Conclusions
Intercellular calcium signaling plays a crucial role in the early expansion and establishment of IAV infection, presenting a potential target for IAV prophylaxis.