2025-09-05 東京大学
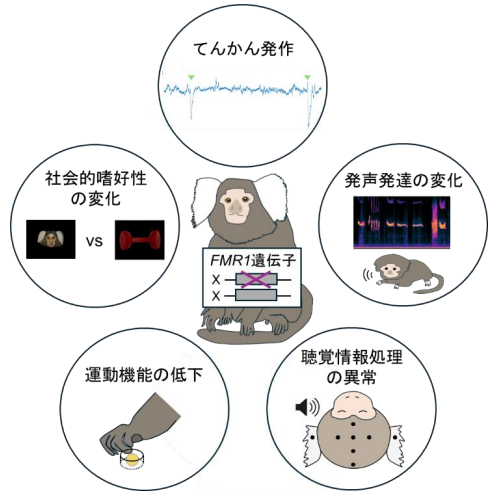
FMR1 変異マーモセットの表現型の概要図
<関連情報>
- https://www.u-tokyo.ac.jp/content/400269575.pdf
- https://www.cell.com/cell-reports/fulltext/S2211-1247(25)00979-9
FMR1変異マーモセットは脆弱X症候群の表現型を示す FMR1 mutant marmosets show fragile X syndrome phenotypes
Maria Harbers ∙ Zefeng Wei ∙ Harumi Nakao ∙ … ∙ Kosuke Itoh ∙ Masanobu Kano ∙ Atsu Aiba
Cell Reports Published:September 4, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2025.116208
Highlights
- Female FMR1+/- mutant marmosets mimic key phenotypes of fragile X syndrome
- An F1 heterozygous marmoset line with a uniform mutation is established for analysis
- Introducing GRM5 gene mutations in FMR1 mutant marmosets rescues the phenotype
Summary
Fragile X syndrome (FXS) is the foremost monogenic cause of autism spectrum disorder and intellectual disability, caused by FMR1 gene silencing. Here, we report that common marmosets carrying FMR1 mutation, a non-human primate model for FXS, share common features in behavioral and molecular phenotypes with patients with FXS. Founder mutants with markedly reduced fragile X messenger ribonucleoprotein expression display hyperactivity, spontaneous seizures, and transcriptome changes in synapse-related genes that overlap with those reported in patients with FXS. Although spontaneous seizures in these mutants lead to postnatal lethality, the lethality is rescued by introducing mutations into the GRM5 gene, suggesting that elevated mGluR5 signaling contributes to the phenotype. F1 heterozygous females carrying a uniform mutation exhibit phenotypes associated with FXS, including alterations in vocal development and social preferences, electroencephalographic abnormalities, and impaired motor skills. Thus, female marmosets heterozygous for the FMR1 mutation represent a valuable translational model for investigating FXS mechanisms and potential therapeutic strategies.