2025-09-22 コロンビア大学
<関連情報>
- https://www.publichealth.columbia.edu/news/metabolic-markers-may-predict-breast-cancer-high-risk-women
- https://breast-cancer-research.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13058-024-01896-5
血漿メタボロミクスプロファイルと乳がんリスク Plasma metabolomics profiles and breast cancer risk
Hui-Chen Wu,Yunjia Lai,Yuyan Liao,Maya Deyssenroth,Gary W. Miller,Regina M. Santella & Mary Beth Terry
Breast Cancer Research Published:09 October 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1186/s13058-024-01896-5
Abstract
Background
Breast cancer (BC) is the most common cancer in women and incidence rates are increasing; metabolomics may be a promising approach for identifying the drivers of the increasing trends that cannot be explained by changes in known BC risk factors.
Methods
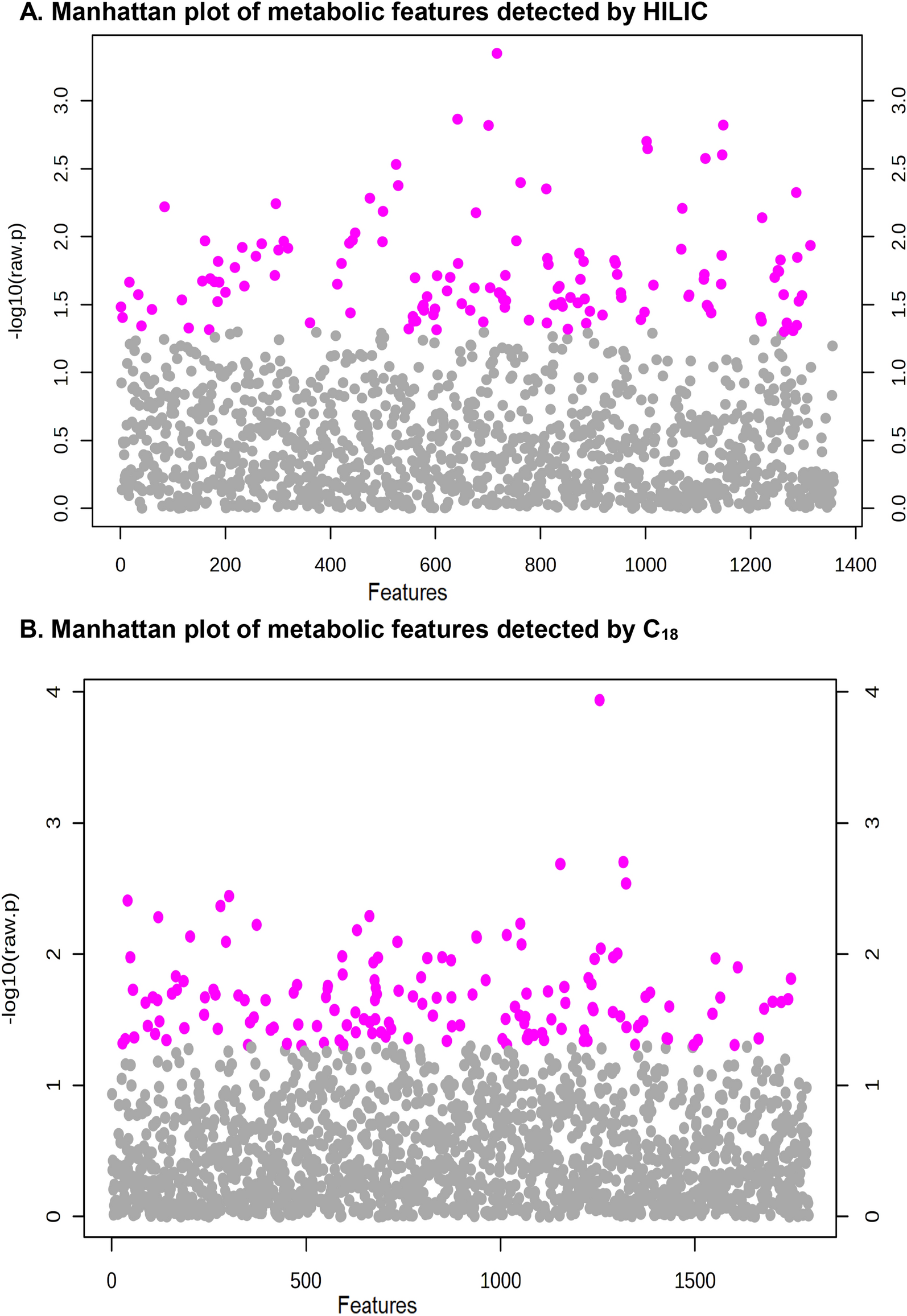
We conducted a nested case–control study (median followup 6.3 years) within the New York site of the Breast Cancer Family Registry (BCFR) (n = 40 cases and 70 age-matched controls). We conducted a metabolome-wide association study using untargeted metabolomics coupling hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC) and C18 chromatography with high-resolution mass spectrometry (LC-HRMS) to identify BC-related metabolic features.
Results
We found eight metabolic features associated with BC risk. For the four metabolites negatively associated with risk, the adjusted odds ratios (ORs) ranged from 0.31 (95% confidence interval (CI): 0.14, 0.66) (L-Histidine) to 0.65 (95% CI: 0.43, 0.98) (N-Acetylgalactosamine), and for the four metabolites positively associated with risk, ORs ranged from 1.61 (95% CI: 1.04, 2.51, (m/z: 101.5813, RT: 90.4, 1,3-dibutyl-1-nitrosourea, a potential carcinogen)) to 2.20 (95% CI: 1.15, 4.23) (11-cis-Eicosenic acid). These results were no longer statistically significant after adjusting for multiple comparisons. Adding the BC-related metabolic features to a model, including age, the Breast and Ovarian Analysis of Disease Incidence and Carrier Estimation Algorithm (BOADICEA) risk score improved the accuracy of BC prediction from an area under the curve (AUC) of 66% to 83%.
Conclusions
If replicated in larger prospective cohorts, these findings offer promising new ways to identify exposures related to BC and improve BC risk prediction.