2025-10-07 理化学研究所

少数の細胞層を介する情報伝達において情報損失を最小化する仕組み
<関連情報>
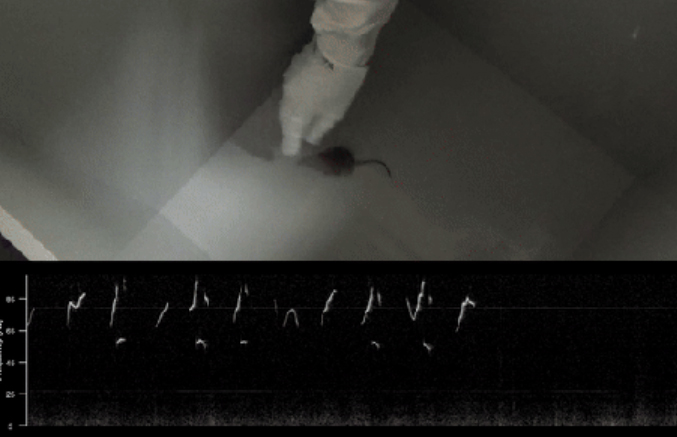
門脈苔状細胞による鋭い波紋の分布閾値下表現 Distributed subthreshold representation of sharp wave-ripples by hilar mossy cells
Ayako Ouchi ,Taro Toyoizumi,Nobuyoshi Matsumoto,Yuji Ikegaya
eLife Published:Oct 7, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.97270
Abstract
In neural information processing, the nervous system transmits neuronal activity between layers of neural circuits, occasionally passing through small layers composed only of sparse neurons. Hippocampal hilar mossy cells (MCs) constitute such a typical bottleneck layer. However, how efficient information encoding is achieved within such constrained layers remains poorly understood. To address this, we focused on sharp wave-ripples (SWRs) – synchronous neural events originating in the CA3 region – and investigated functional diversity within MC populations using in vivo/in vitro patch-clamp recordings in mice. By combining machine learning algorithms, we developed a model to predict CA3 SWR waveforms based on the synaptic response waveforms of MCs, suggesting that SWR-related information is indeed encoded in their subthreshold activity. While individual MCs were generally associated with specific SWR clusters, partial overlap across some MCs was also observed, indicating that CA3 activity is distributed across the MC population. Our findings suggest that CA3 SWR activity is represented in a pseudo-orthogonal manner across MC populations, allowing the small MC layer to effectively compress and relay hippocampal information.