2025-10-28 京都大学
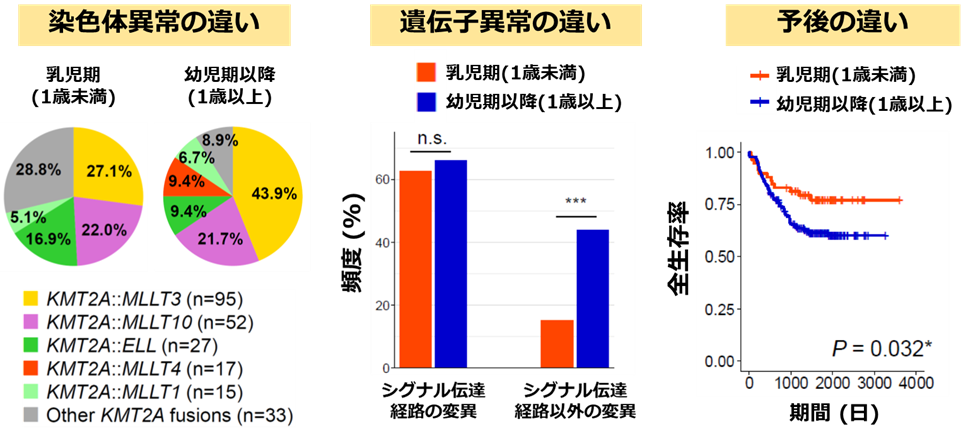
KMT2A 再構成 AML の発症年齢によるゲノム異常パターンや予後の違い
<関連情報>
- https://www.kyoto-u.ac.jp/ja/research-news/2025-10-28-1
- https://www.kyoto-u.ac.jp/sites/default/files/2025-10/2510_Haematologica_Matsuo_relj%20web-2dfe15a051c689ed32d5868b1c925db7.pdf
- https://haematologica.org/article/view/12959
小児 KMT2A 再構成 AML における年齢特異的な変異プロファイルと予後への影響 Age-specific mutation profiles and their prognostic implications in pediatric KMT2A-rearranged acute myeloid leukemia
Kota Shoji,Kenichi Yoshida,Shinju Iyoda,Moe Ishikawa,Miu Tanaka,Michidai Nobe,Nijika Saito,Yuto Shino,Yasuhito Nannya,Genki Yamato,Shinichi Tsujimoto,Norio Shiba,Yasuhide Hayashi,Yusuke Shiozawa,Yuichi Shiraishi,Kenichi Chiba,Ai Okada,Hiroko Tanaka,Satoru Miyano,Yuhki Koga,Hiroaki Goto,Kiminori Terui,Etsuro Ito,Nobutaka Kiyokawa,Daisuke Tomizawa,Takashi Taga,Hiroshi Moritake,Akio Tawa,Junko Takita,Momoko Nishikori,Souichi Adachi,Seishi Ogawa,Hidemasa Matsuo
Haematologica Published:Oct 23, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2025.288481
Abstract
Driver mutations in KMT2A-rearranged (KMT2A-r) have been identified in acute myeloid leukemia (AML); however, age-related differences in their frequency and prognostic factors remain unclear. In this study, we report age-specific mutation profiles and outcomes in pediatric patients with KMT2A-r AML. In 239 cases of KMT2A-r AML, infants (<1 year, n = 59) showed a significantly higher event-free survival (EFS) and overall survival (OS) compared with children (≥1 year, n = 180). Conversely, in 538 cases of non-KMT2A-r AML, infants exhibited a significantly lower EFS and OS than children. KMT2A::MLLT4 was only detected in children with KMT2A-r AML and was associated with a poor prognosis. In KMT2A-r AML, mutations in signaling pathway genes, such as KRAS, were frequently detected in infants and children. However, the frequency of non-signaling pathway mutations was significantly higher in children. Moreover, non-signaling pathway mutations had no significant effect on the prognosis in infants and children, whereas KRAS mutations were associated with poor prognosis in both groups. Multivariate analysis identified older age, a high white blood cell count, KMT2A::MLLT4, and KRAS mutations as independent adverse prognostic factors for both EFS and OS. These age-specific mutation profiles suggest distinct disease mechanisms across age groups and may help refine risk stratification and treatment strategies for pediatric KMT2A-r AML.


