2025-11-18 金沢大学,科学技術振興機構,東京科学大学
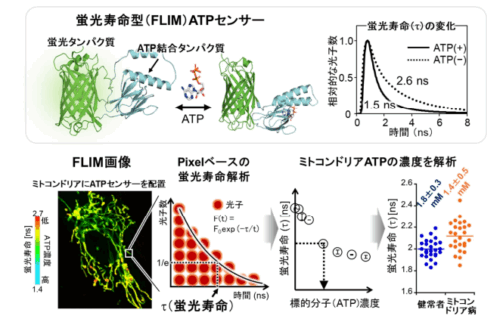
図 1 ATP 濃度を蛍光寿命に変換できる ATP センサー(qMaLioffG)。検量線(蛍光寿命と ATP 濃度)を用いて、ピクセル毎の蛍光寿命値を算出、ATP 濃度情報を得ることができる。ミトコンドリア病によって ATP 産生能に障害がある細胞の ATP 濃度を定量解析した(出版社から許可を得て掲載論文の図を改変)。
<関連情報>
- https://www.jst.go.jp/pr/announce/20251118-3/index.html
- https://www.jst.go.jp/pr/announce/20251118-3/pdf/20251118-3.pdf
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-64946-2
qMaLioffG: 細胞内ATPの定量的イメージングを可能にする遺伝子コード化された緑色蛍光寿命ベースの指標 qMaLioffG: a genetically encoded green fluorescence lifetime-based indicator enabling quantitative imaging of intracellular ATP
Satoshi Arai,Hideki Itoh,Cong Quang Vu,Loan Thi Ngoc Nguyen,Mizuho Nakayama,Masanobu Oshima,Atsuya Morita,Kazuko Okamoto,Satoru Okuda,Aki Teranishi,Madori Osawa,Yoshiteru Tamura,Shigeaki Nonoyama,Megumi Takuma,Toshinori Fujie,Satya Ranjan Sarker,Thankiah Sudhaharan,Akihiro Furube,Tetsuro Katayama,Taketoshi Kiya,E. Birgitte Lane & Tetsuya Kitaguchi
Nature Communications Published:13 November 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-64946-2
Abstract
Genetically encoded indicators that can detect concentrations of metabolites and signalling molecules through fluorescence lifetime changes are gaining attention, because they expand the potential for quantitative imaging. These indicators offer advantages over conventional fluorescence intensity-based indicators by minimizing artifacts such as variations in indicator concentration, cellular morphological changes, and focus drift. However, the availability of fluorescence lifetime-based genetically encoded indicators remains limited, particularly those compatible with the widely used conventional 488 nm laser in microscopy. Here, we introduce qMaLioffG, a single green fluorescent protein-based ATP indicator that exhibits a substantial fluorescence lifetime shift (1.1 ns) within physiologically relevant ATP concentrations. This enables quantitative imaging of ATP levels in the cytoplasm and mitochondria under steady-state conditions across various cell types, providing insights into ATP distribution. We demonstrate that qMaLioffG can be used in multicellular systems, applying it to Drosophila brain and HeLa cell spheroids to reveal spatially heterogeneous ATP levels.