2025-11-20 ミュンヘン大学(LMU)
<関連情報>
- https://www.lmu.de/en/newsroom/news-overview/news/ai-improves-lung-cancer-diagnostics.html
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-65783-z
AIを活用した空間細胞フェノミクスが非小細胞肺がんのリスク層別化を強化 AI-powered spatial cell phenomics enhances risk stratification in non-small cell lung cancer
Simon Schallenberg,Gabriel Dernbach,Sharon Ruane,Philipp Jurmeister,Cornelius Böhm,Kai Standvoss,Sandip Ghosh,Marco Frentsch,Mihnea P. Dragomir,Philipp G. Keyl,Corinna Friedrich,Il-Kang Na,Sabine Merkelbach-Bruse,Alexander Quaas,Nikolaj Frost,Kyrill Boschung,Winfried Randerath,Georg Schlachtenberger,Matthias Heldwein,Ulrich Keilholz,Khosro Hekmat,Jens-Carsten Rückert,Reinhard Büttner,Angela Vasaturo,… Frederick Klauschen
Nature Communications Published:03 November 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-65783-z
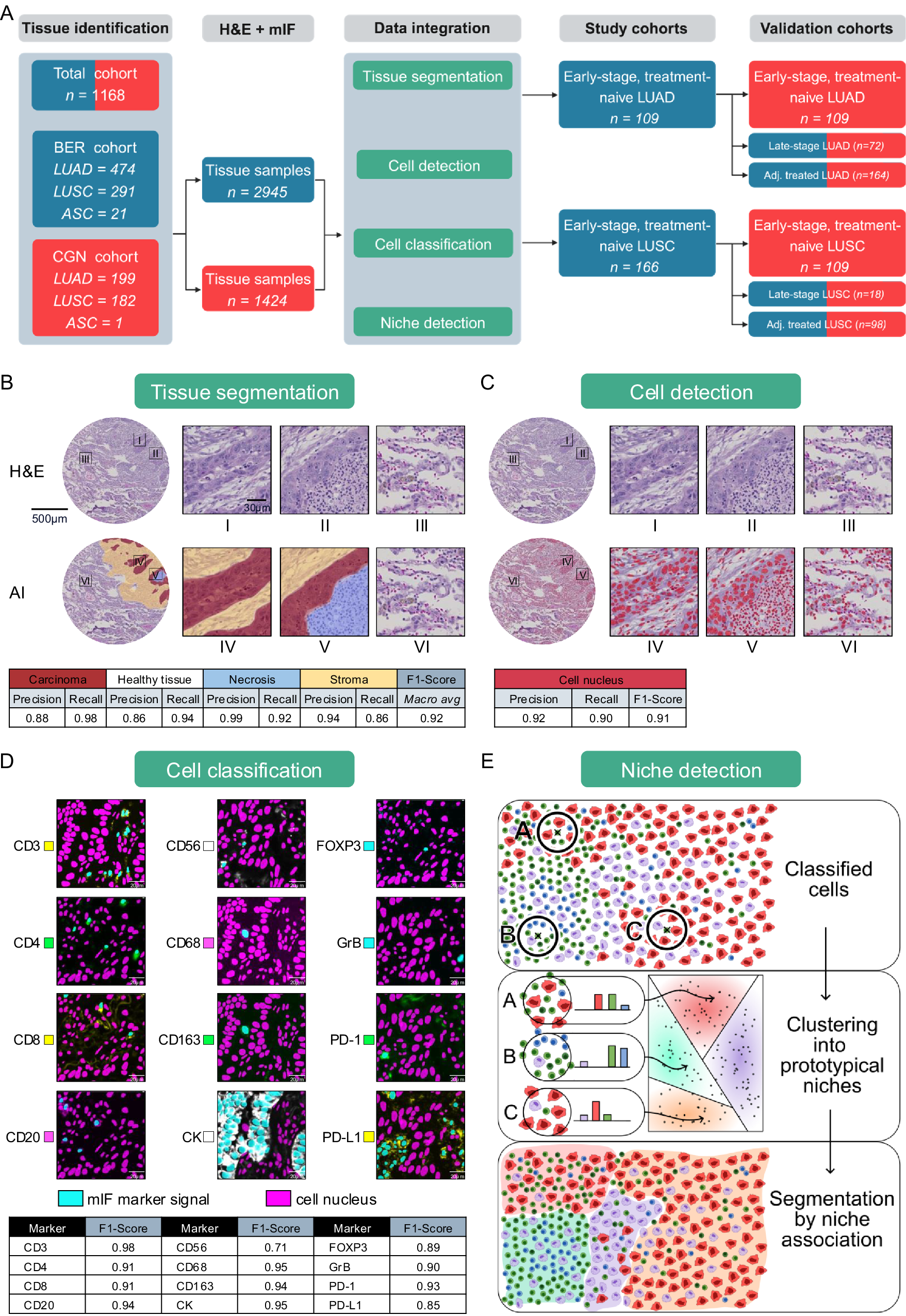
Abstract
Risk stratification remains a critical challenge in non-small cell lung cancer patients for optimal therapy selection. In this study, we develop an artificial intelligence-powered spatial cellomics approach that combines histology, multiplex immunofluorescence imaging and multimodal machine learning to characterize the complex cellular relationships of 43 cell phenotypes in the tumor microenvironment in a real-world retrospective cohort of 1168 non-small cell lung cancer patients from two large German cancer centers. The model identifies cell niches associated with survival and achieves a 14% and 47% improvement in risk stratification in the two main non-small cell lung cancer subtypes, lung adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, respectively, combining niche patterns with conventional cancer staging. Our results show that complex immune cell niche patterns identify potentially undertreated high-risk patients qualifying for adjuvant therapy. Our approach highlights the potential of artificial intelligence powered multiplex imaging analyses to better understand the contribution of the tumor microenvironment to cancer progression and to improve risk stratification and treatment selection in non-small cell lung cancer.