2025-11-27 国立遺伝学研究所
<関連情報>
- https://www.nig.ac.jp/nig/ja/2025/11/research-highlights_ja/pr20251127.html
- https://www.nig.ac.jp/nig/images/research_highlights/PR20251127.pdf
- https://academic.oup.com/nar/article/53/22/gkaf1010/8343520
ヒストンシャペロンCAF-1は、複製と連動したDNA二本鎖切断修復中に、出芽酵母リボソームDNAの相同組換えを介した不安定性を防ぐ The histone chaperone CAF-1 prevents homologous recombination-mediated instability of the budding yeast ribosomal DNA during replication-coupled DNA double-strand break repair
Hajime Futami, Tsugumi Yamaji, Yuko Katayama, Nanase Arata, Mio Nagura, Takehiko Kobayashi, Mariko M Sasaki
Nucleic Acids Research Published:27 November 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaf1010
Abstract
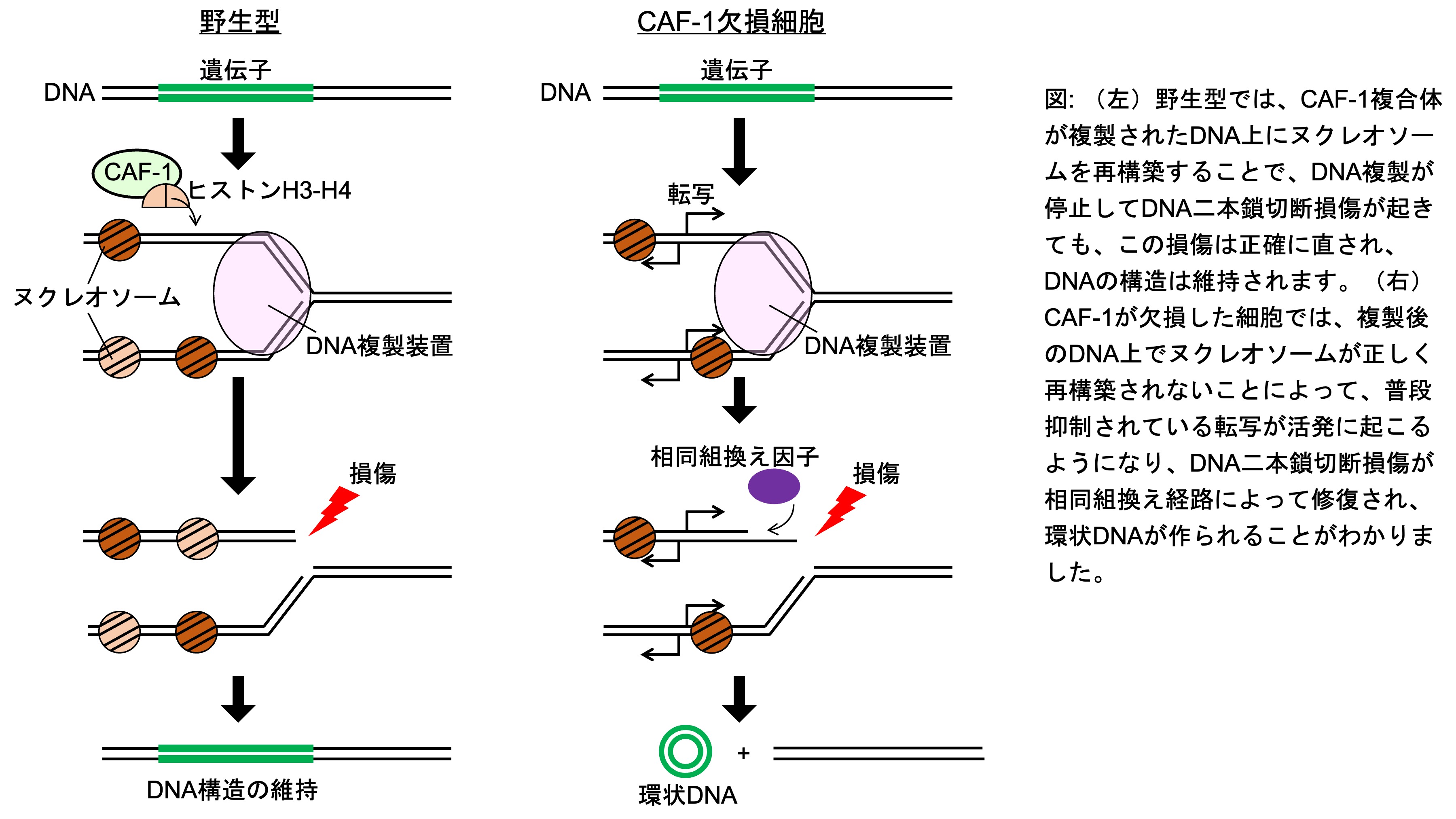
DNA replication-coupled chromatin assembly is crucial to maintain genome integrity. Here, we demonstrate that the absence of the budding yeast histone chaperone CAF-1 induces the production of extrachromosomal ribosomal RNA gene (rDNA) circles (ERCs), accompanied by chromosomal rDNA copy number changes, in a manner dependent on Fob1-mediated DNA replication fork arrest in the rDNA, the homologous recombination (HR) protein Rad52, and its interaction with proliferating cell nuclear antigen. In the caf-1 mutant, ERC production is triggered partly by increased transcription from the regulatory promoter E-pro, but is also affected by defects independent of E-pro misregulation. Absence of CAF-1 accumulates resected DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) formed at arrested replication forks, repair of which leads to enhanced ERC formation. CAF-1 deficiency causes partial defects in lagging strand synthesis coupled to nucleosome spacing in the rDNA. Our findings suggest that CAF-1 suppresses HR-mediated rDNA instability during repair of replication-coupled DSBs.