2025-12-16 成育医療研究センター
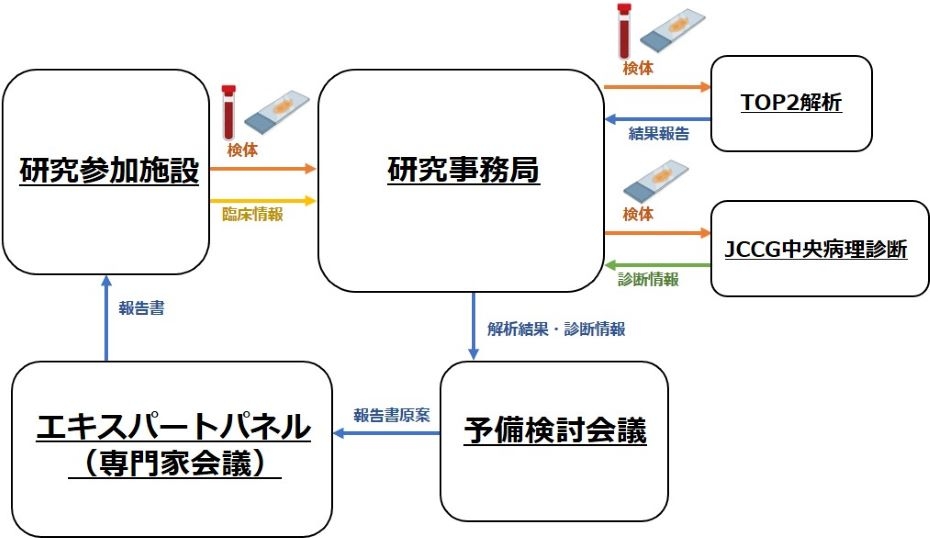
【図1:JCCG-TOP2研究の概要】
<関連情報>
- https://www.ncchd.go.jp/press/2025/1216.html
- https://www.ncchd.go.jp/press/2025/1216.pdf
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/cas.70249
小児固形腫瘍のDNA/RNAデュアルパネルを用いたゲノムプロファイリング:JCCG-TOP2研究 Genomic Profiling of Pediatric Solid Tumors With a Dual DNA/RNA Panel: JCCG-TOP2 Study
Kayoko Tao, Takako Yoshioka, Miho Kato, Kazuyuki Komatsu, Shinichi Tsujimoto, Kenichi Sakamoto, Kazuki Tanimura, Minako Sugiyama, Masahiro Sekiguchi, Yoshiko Nakano …
Cancer Science Published: 17 November 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.70249
ABSTRACT
To develop an optimized genomic medicine platform for pediatric cancers, a nationwide cancer genome profiling project was conducted from January 2022 to February 2023 in collaboration with the Japan Children’s Cancer Group. This prospective observational study analyzed matched blood and FFPE tumor samples from patients aged 0–29 years with solid tumors. Genomic analysis used the TOP2 hybrid capture–enrichment system, targeting 737 and 455 genes in the DNA and RNA panels, along with allele-specific genome copy number alterations. A total of 210 patients from 50 institutions were enrolled across Japan (median age, 8 years; range, 0–25). Of these, 154 (77%) were enrolled at diagnosis or during/after initial treatment and 56 (27%) at disease progression or relapse. The TOP2 findings had great benefits in clarifying the diagnosis of pediatric solid tumors. Among the 204 patients with genomic results, 147 (72%) had potentially actionable findings, including diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic findings in 111 (54%), 61 (30%), and 64 (31%), respectively. Oncogenic fusions were noted in 45 (23%) patients. A copy number alteration was identified in at least one genomic region in 170 (83%) patients. Two patients exhibited a high tumor mutation burden. Seventeen (8%) patients harbored a germline pathogenic/likely pathogenic variant in cancer-predisposing genes. This study highlighted the feasibility of implementing a nationwide precision medicine platform and the clinical utility of the TOP2 system for pediatric cancers. The results support the integration of genomic data into the standard clinical care of pediatric patients with cancer, both at diagnosis and at relapse.